Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Synovial Joint Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Synovial Joint Image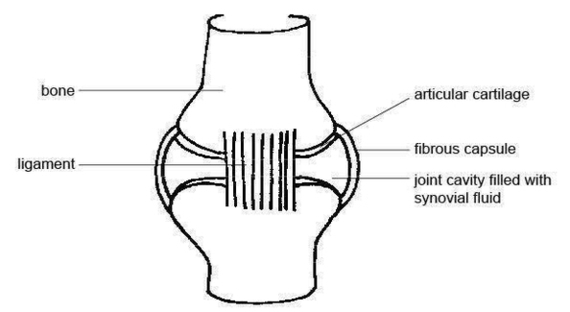
Tag Archives: physiology
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals The Ear Image
Anatomy and physiology of the canine ear The canine ear consists of the pinna, external ear canal, middle ear and inner ear. The external ear is composed of auricular and annular cartilage. The auricular cartilage of the pinna becomes funnel shaped at the opening of the external ear canal. The vertical ear canal runs for about 1 inch, then …
The ear canal contains protective hairs and ear wax ( cerumen ). The middle ear (tympanic cavity) lies behind the eardrum. The middle ear contains three small bones (ossicles) that transmit sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear. The three bones are called the malleus, the incus, and the stapes.
Other than hearing, the main function is to maintain the balance of the body. The hair cells present in the inner ear of mammals help in sensing the position of the body, in accordance with gravity and maintain the equilibrium. Structure of ear comprises three main sections: the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear.
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals The Ear Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals The Ear Image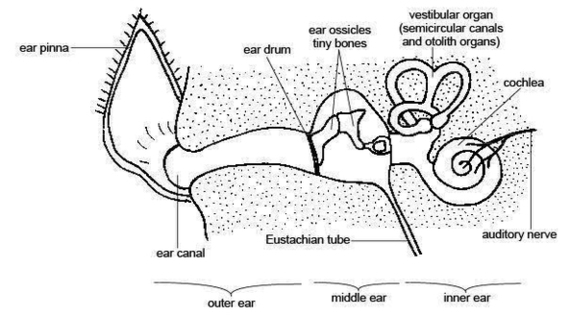
Anatomy And Physiology Pictures Image
87,967 professional anatomy stock photos available royalty-free. Old vintage anatomy charts of the human body. Showing the skeletal system and various muscles, four figures in a row in different orientations SPINE Pain – Male Hurt Backbone isolated on white – REAL Anatomy.
Human Anatomy. Is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy ( Watercolor anatomy organ heart illustration. High quality illustration human body organs heart for education Dog Nervous System – Canis Lupus Familiaris Anatomy – isolated o. N white
Images are “copyright-free as long as they are used for educational purposes” (text from the website). Collection of anatomy illustrations created and shared by Anatomy instructor Alice Roberts. Images, study resources, and interactive modules for the study of anatomy. All are licensed under Creative Commons licenses.
Anatomy And Physiology Pictures Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Anatomy And Physiology Pictures Image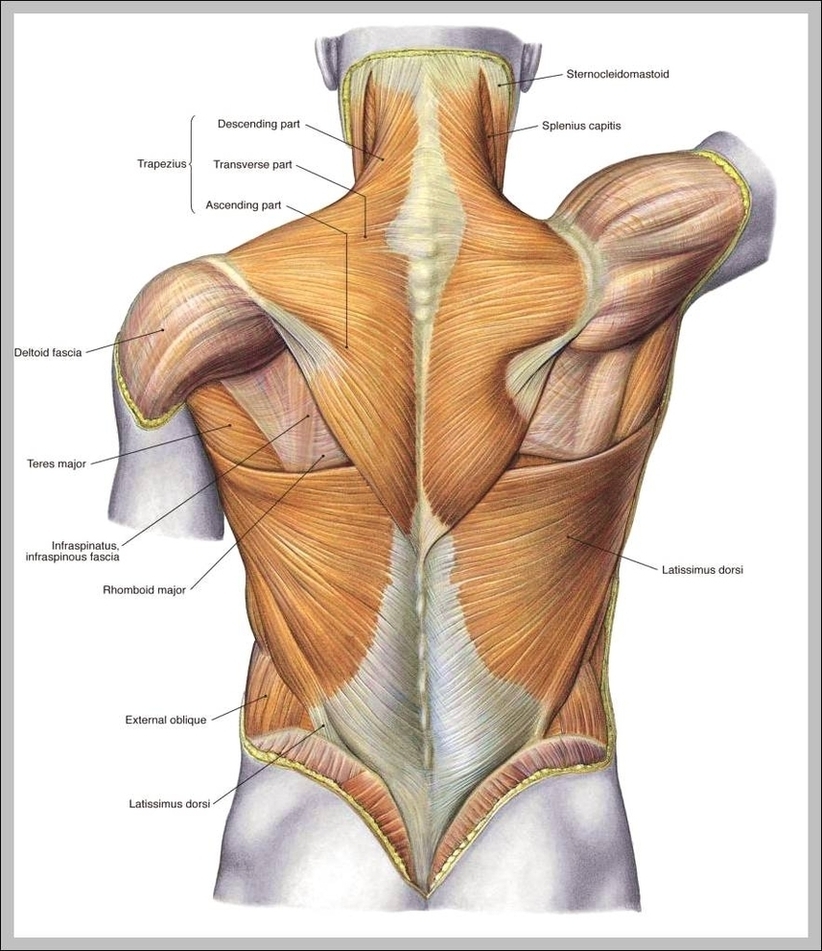
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Structure Of Muscle Image
Here is a nice 50-questions quiz on animal muscles both as gross anatomy and in a microscope. This quiz; however, will focus on the gross anatomy of muscles.
Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. They are primarly responsible for maintaining and changing posture,locomotion as well as movement of internal organs. They are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis.
Different skeletal muscles in animals are described as white and red muscle. These different types of skeletal muscles are recruited depending on whether a fast and short versus steady and prolonged locomotion is needed by the animal.
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Structure Of Muscle Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Structure Of Muscle Image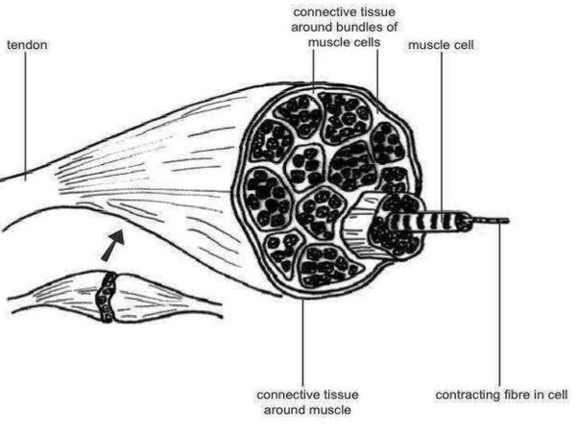
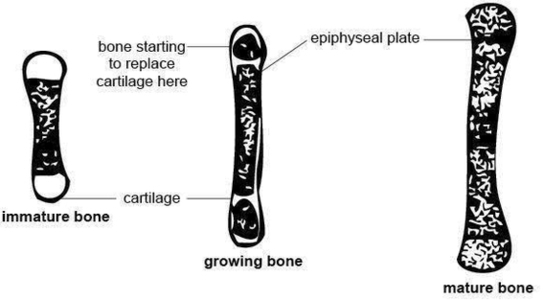
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Growing Bone1 Image
138Anatomy and physiology of domestic animals associated with bone formation, it can occur in other tissues. There are two general classes of bone formation. Intramembranous ossifi cation occurs when bone develops from a fi brous membrane. The fl at bones of the skull and face, the mandible, and the clavicle if present, are formed by this method.
A typical long bone shows the gross anatomical characteristics of bone. The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis (plural = epiphyses), which is filled with spongy bone. Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone.
The dynamic nature of bone means that new tissue is constantly formed, and old, injured, or unnecessary bone is dissolved for repair or for calcium release. The cell responsible for bone resorption, or breakdown, is the osteoclast.
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Growing Bone1 Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Growing Bone1 Image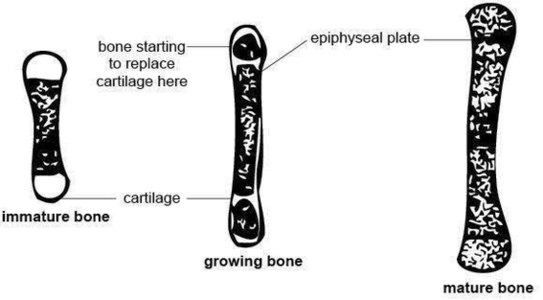
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Growing Bone Image
138Anatomy and physiology of domestic animals associated with bone formation, it can occur in other tissues. There are two general classes of bone formation. Intramembranous ossifi cation occurs when bone develops from a fi brous membrane. The fl at bones of the skull and face, the mandible, and the clavicle if present, are formed by this method.
134Anatomy and physiology of domestic animals long bones. Long bones are characterized by an elongated shaft and somewhat enlarged extremi- ties that bear articular surfaces. Examples of long bones include the humerus, radius, femur, tibia, metacarpals, and metatarsals. •Short bones.
A typical long bone shows the gross anatomical characteristics of bone. The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis (plural = epiphyses), which is filled with spongy bone. Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone.
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Growing Bone Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Growing Bone Image