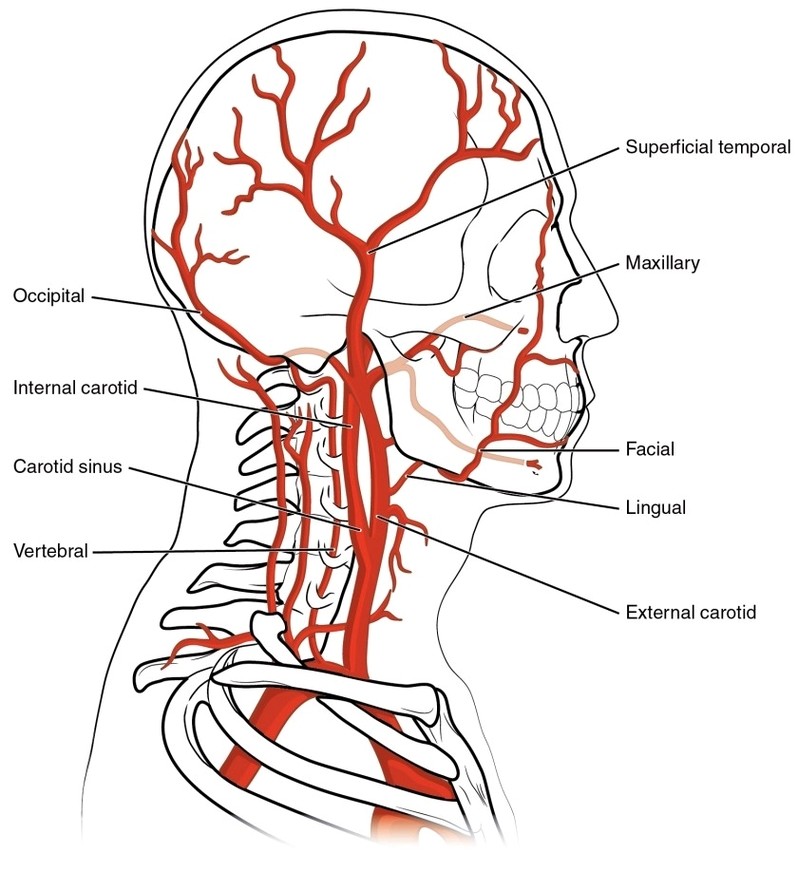
Common Carotid Artery
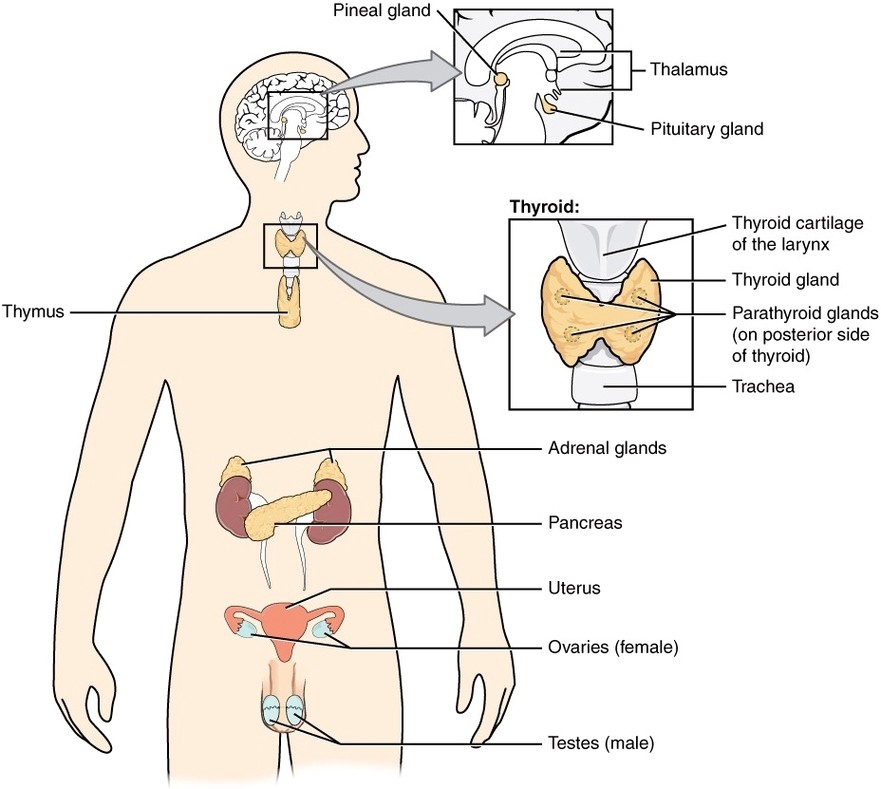
Endocrine System
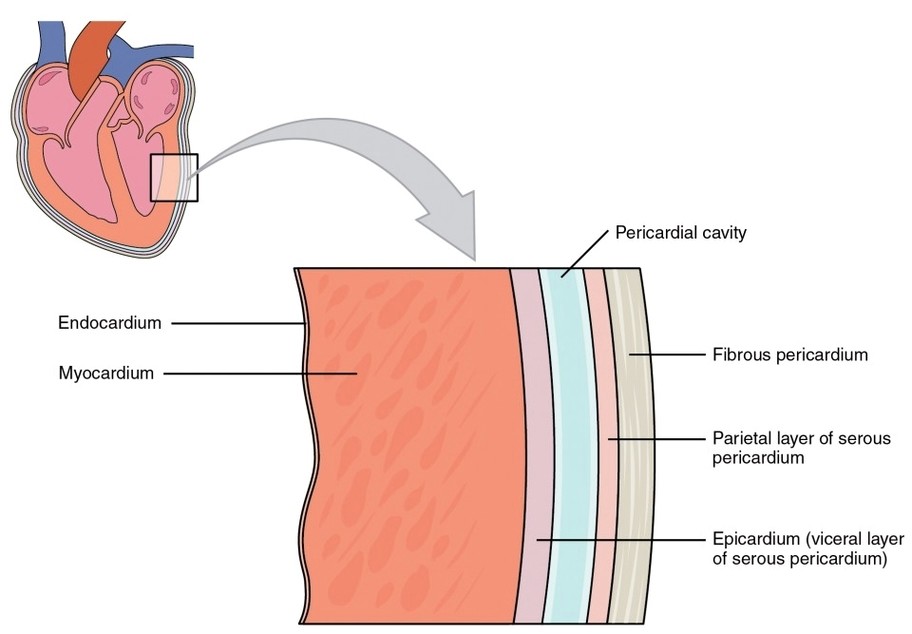
Heart Wall
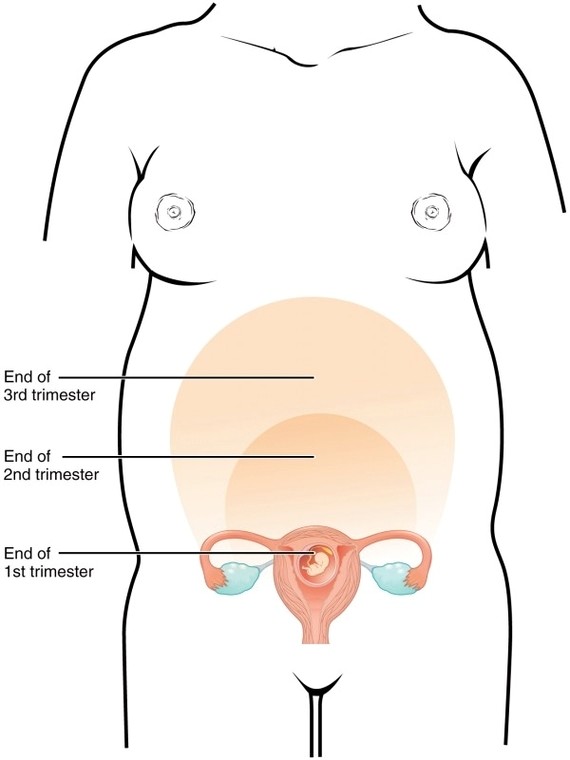
Size of Uterus Throughout Pregnancy
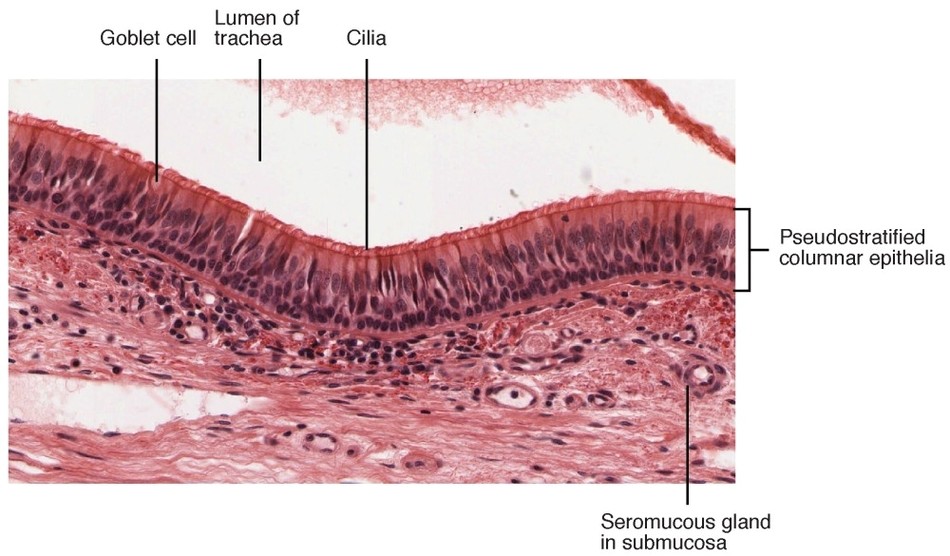
Pseudostratified Epithelium
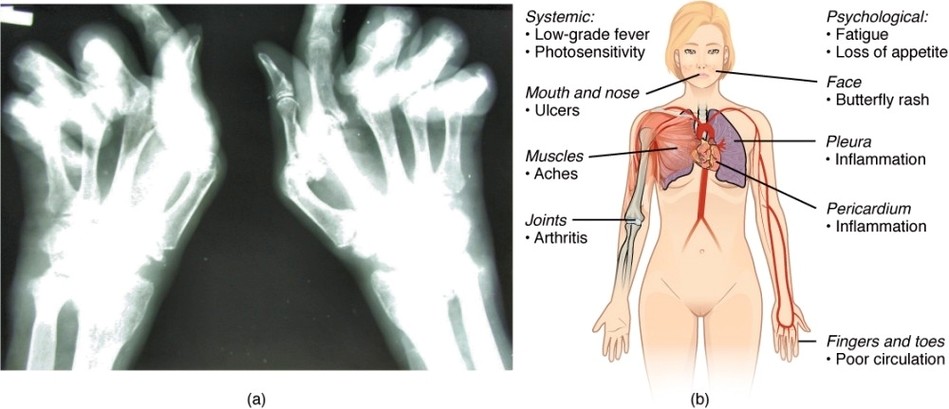
Autoimmune Disorders Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus
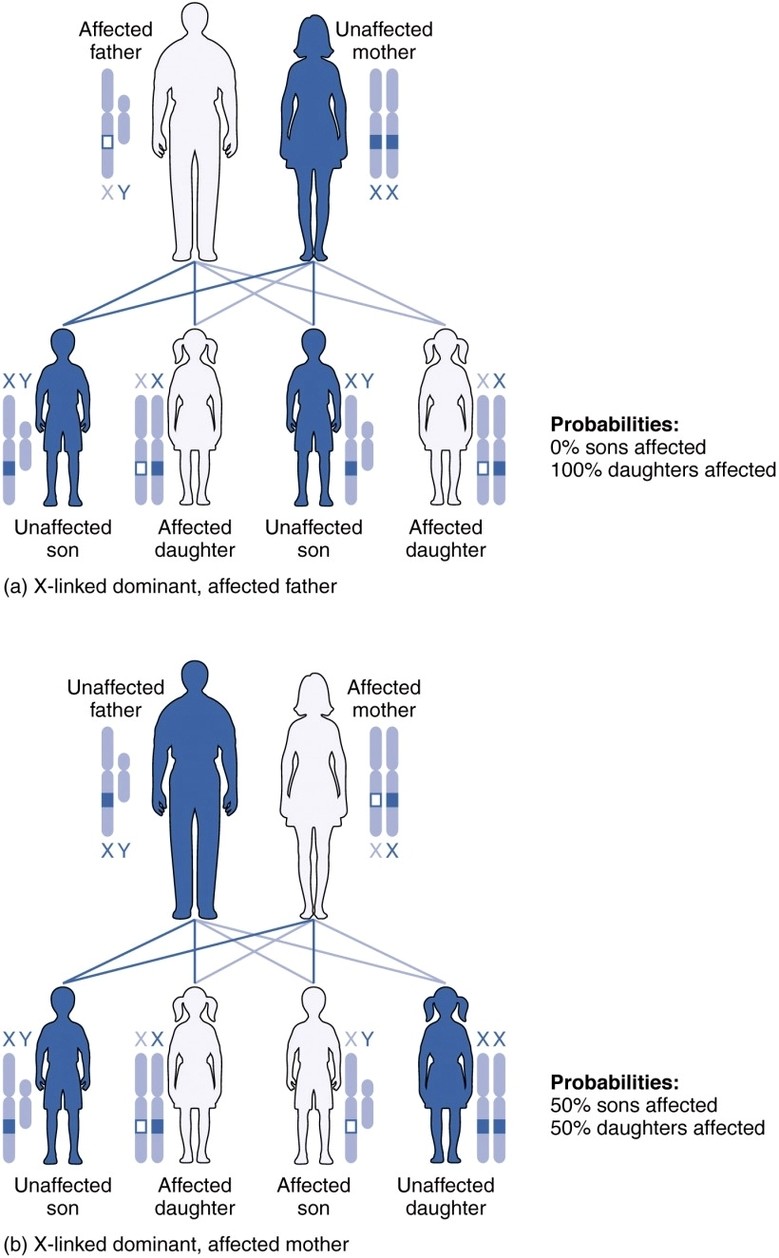
X linked Dominant Inheritance new
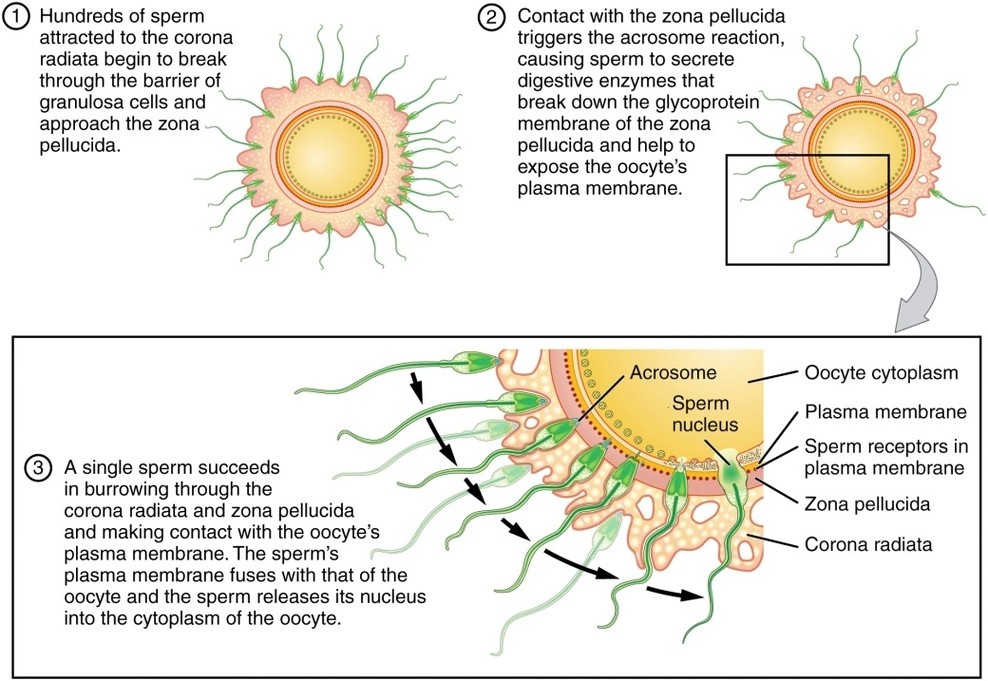
Sperm Fertilization
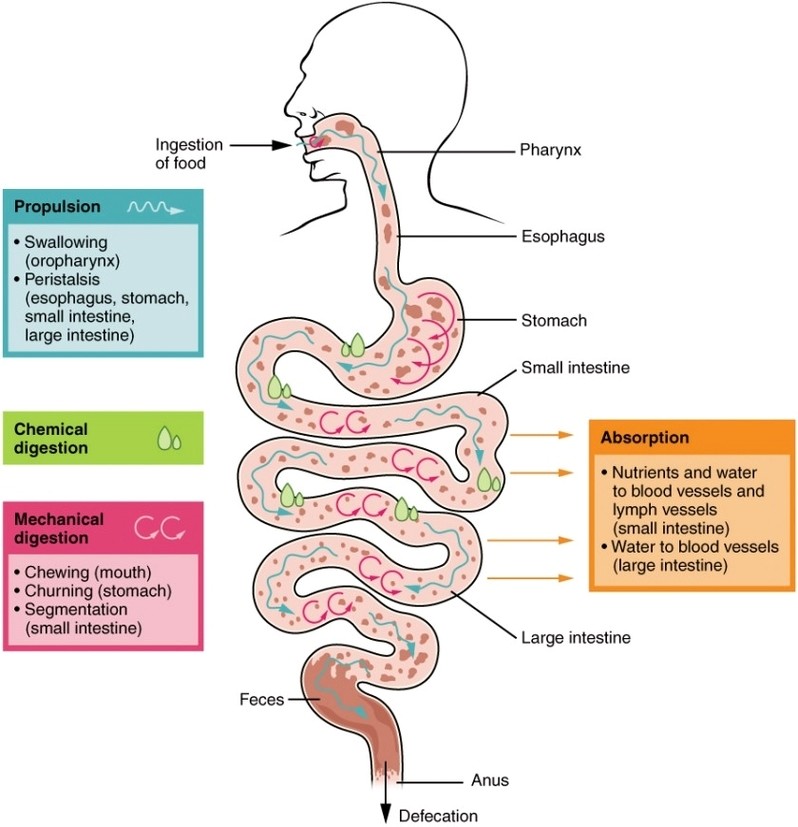
Digestion of Proteins Physiology
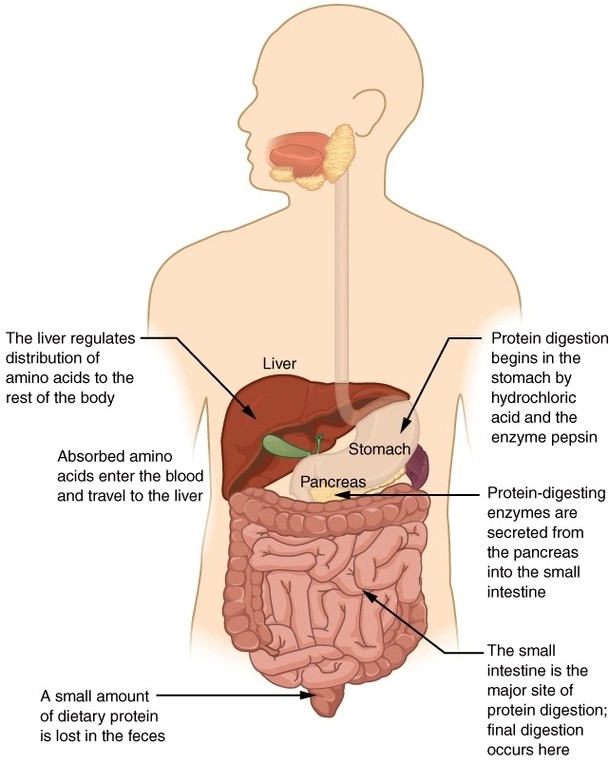
Digestion of Proteins Physiology: Protein digestion begins in the stomach, where the enzyme pepsin breaks down complex proteins into smaller peptides. This process continues in the small intestine, where pancreatic enzymes like trypsin and chymotrypsin further degrade peptides into amino View Diagram Digestion of Proteins Physiology
Blood Flow in the Nephron
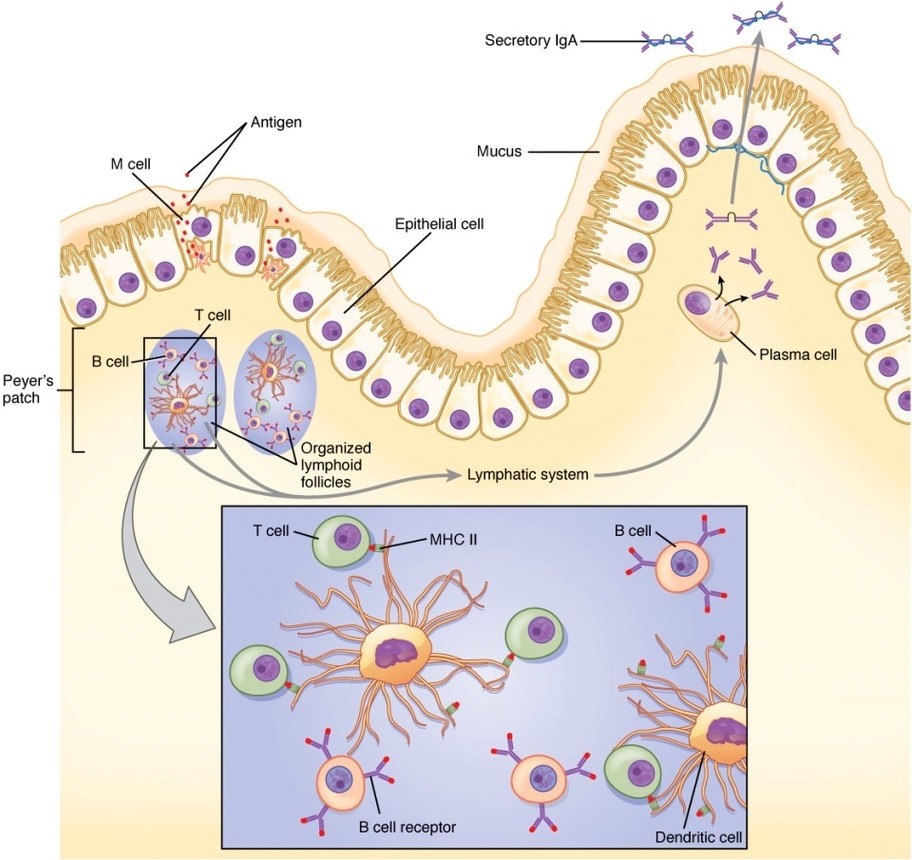
IgA Immunity
Microscopic Anatomy of Liver
NEW-6-4-13