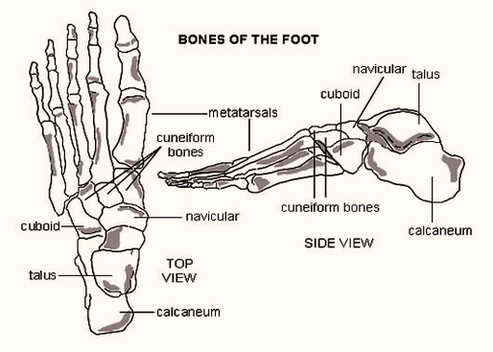
The skeletal structure of the foot is similar to that of the hand but, because the foot bears more weight, it is stronger but less movable. The bones of the foot are organized into the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. The foot begins at the lower end of the tibia and fibula, the two bones of the lower leg. Foot Bones Diagram Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Foot Bones Diagram Image and explains the details of Foot Bones Diagram Image.
Foot Bones Diagram Image