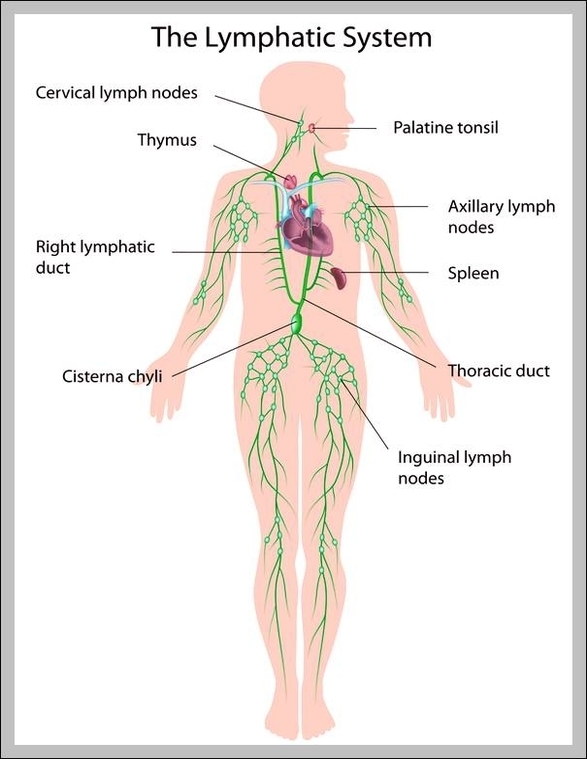
Lymph very closely resembles the plasma found in the veins: it is a mixture of about 90% water and 10% solutes such as proteins, cellular waste products, dissolved gases, and hormones. Lymph may also contain bacterial cells that are picked up from diseased tissues and the white blood cells that fight these pathogens. Picture Of Lymphatic System Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Picture Of Lymphatic System and explains the details of Picture Of Lymphatic System.
Picture Of Lymphatic System