Category Archives: Body Parts
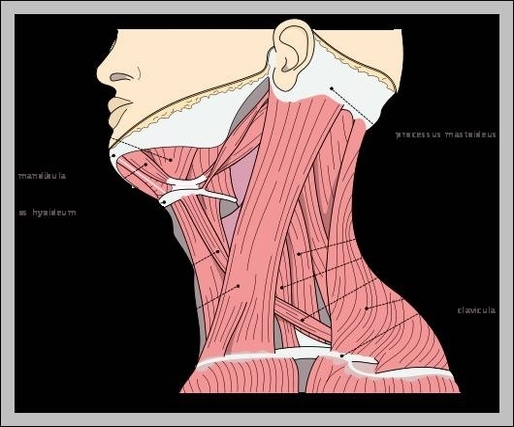
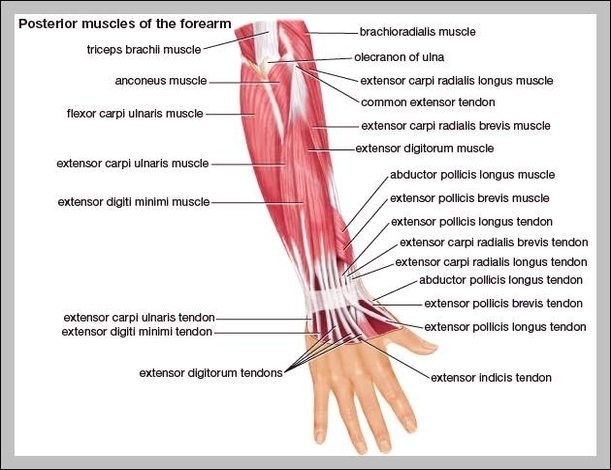
Name Of Neck Muscles
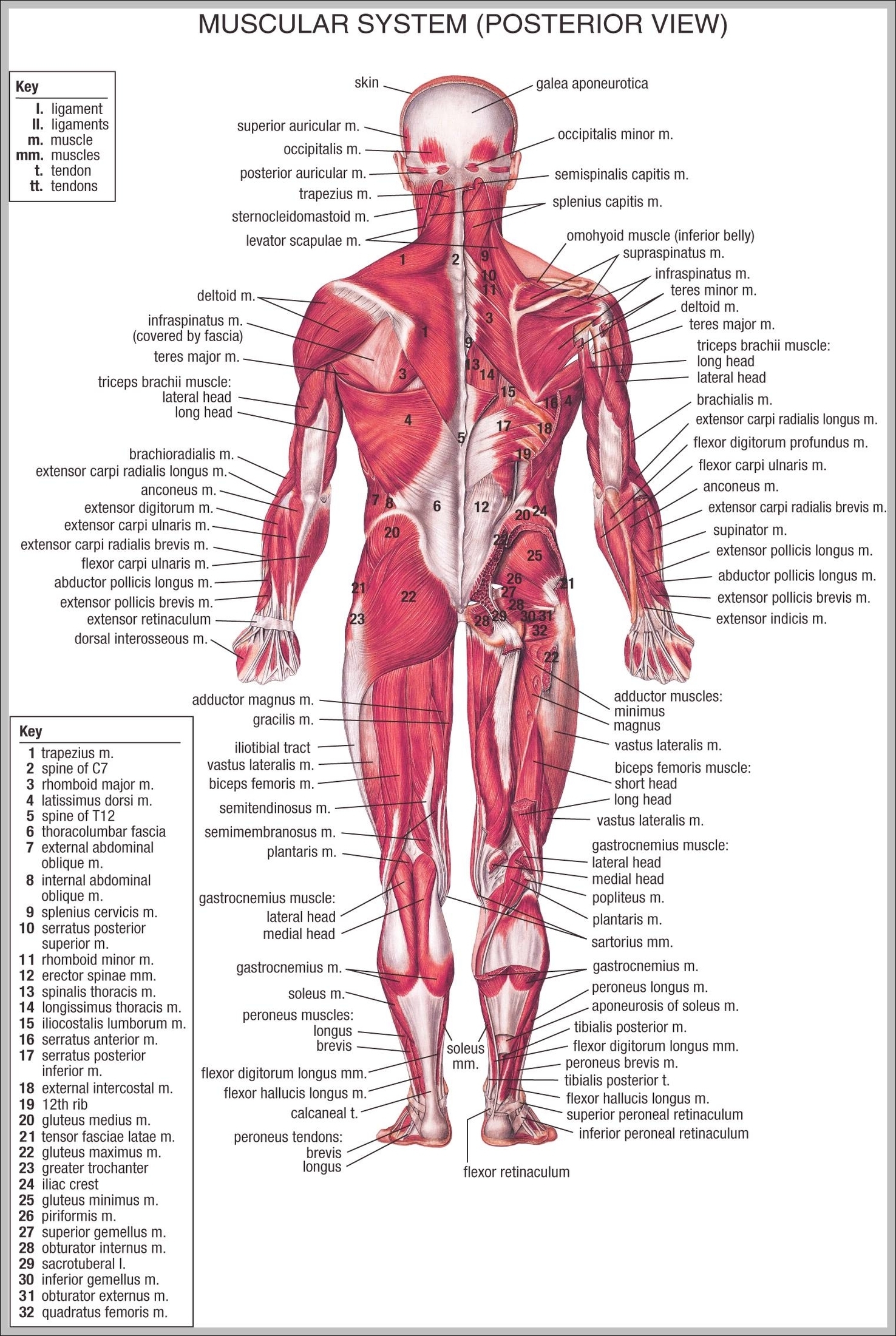
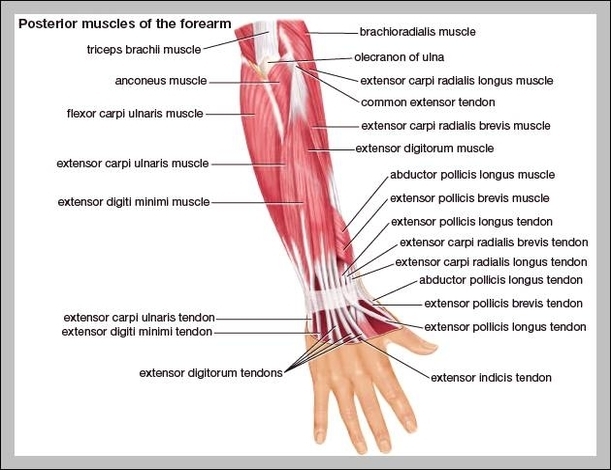
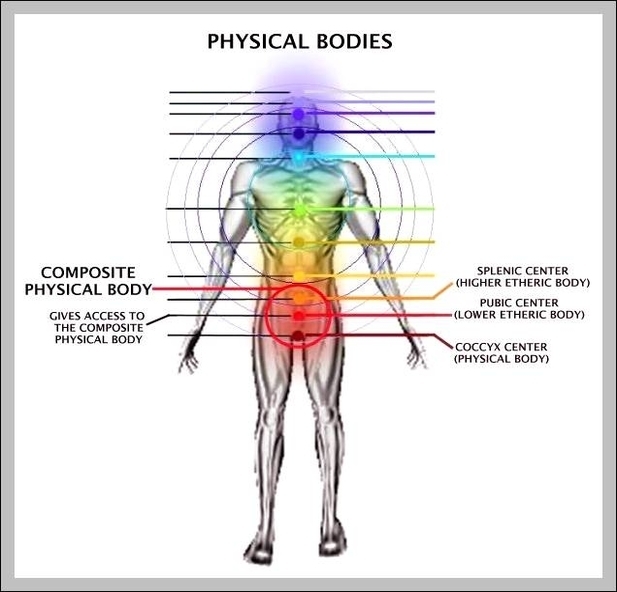
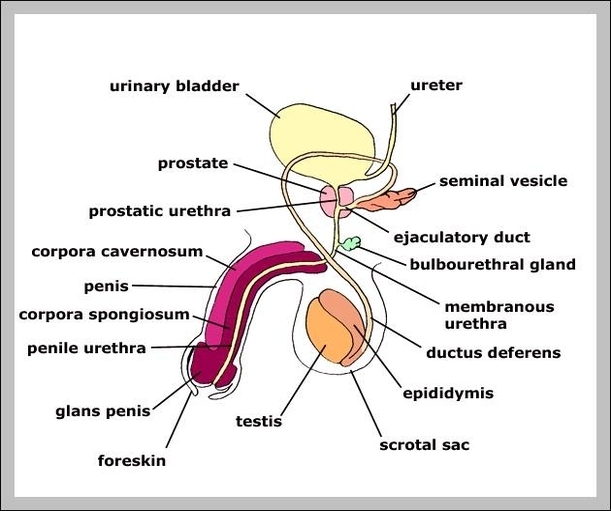
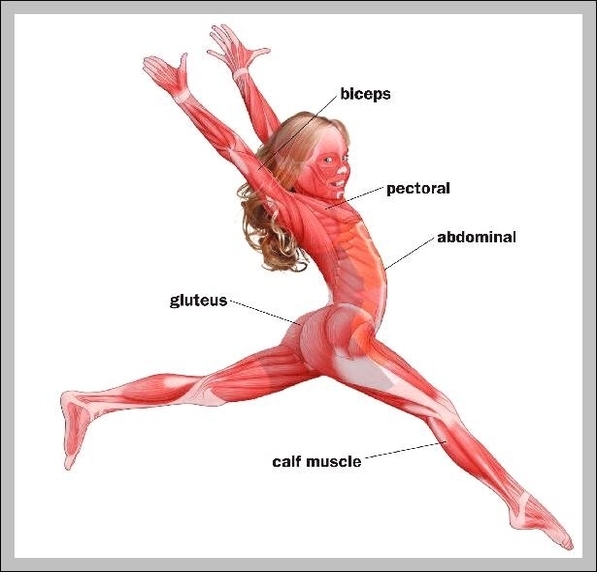
Muscular System Parts
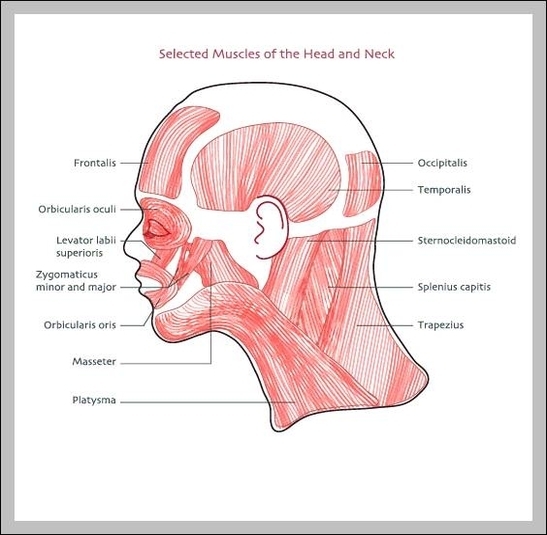
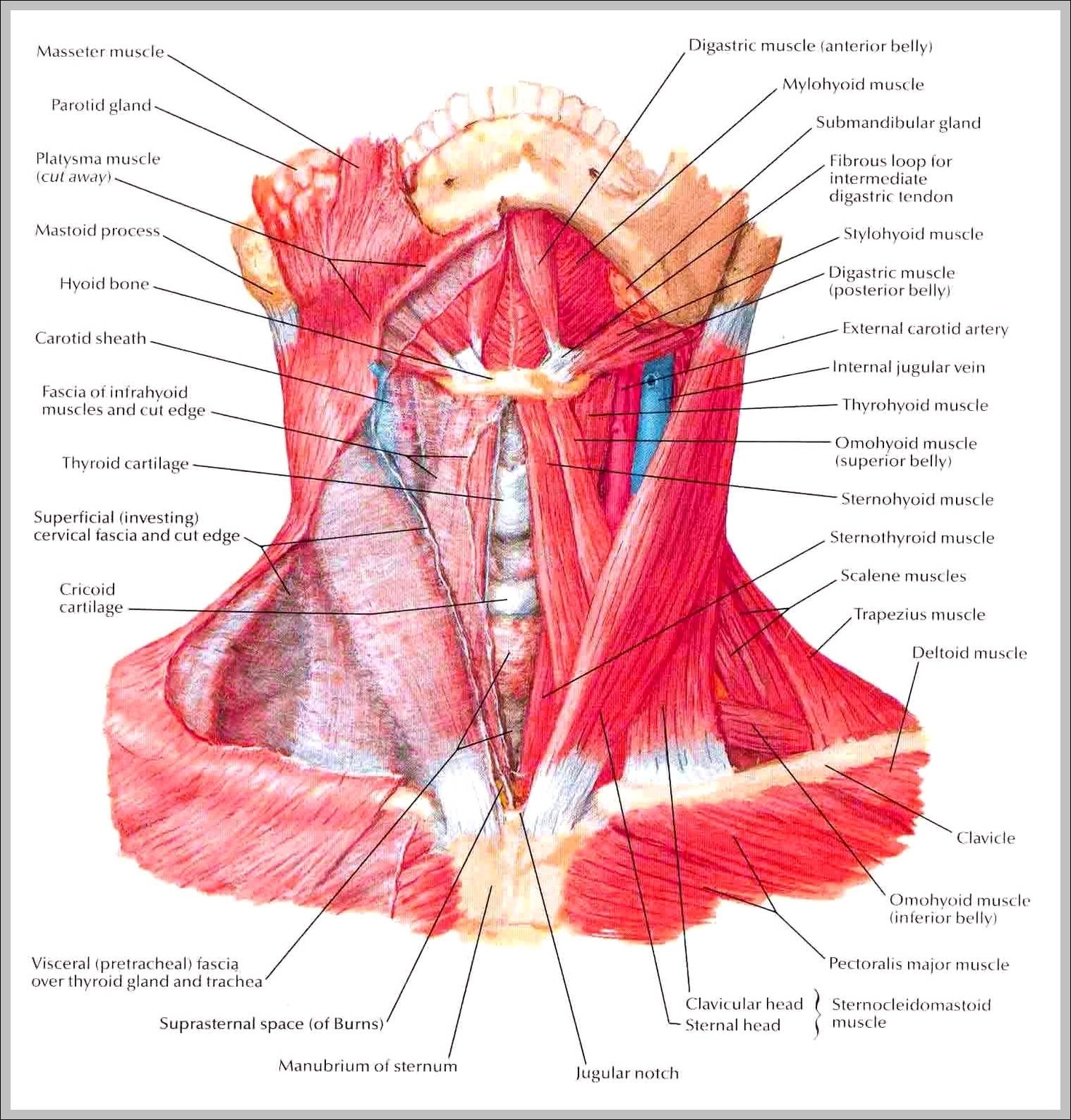
Muscles Of The Neck And Head
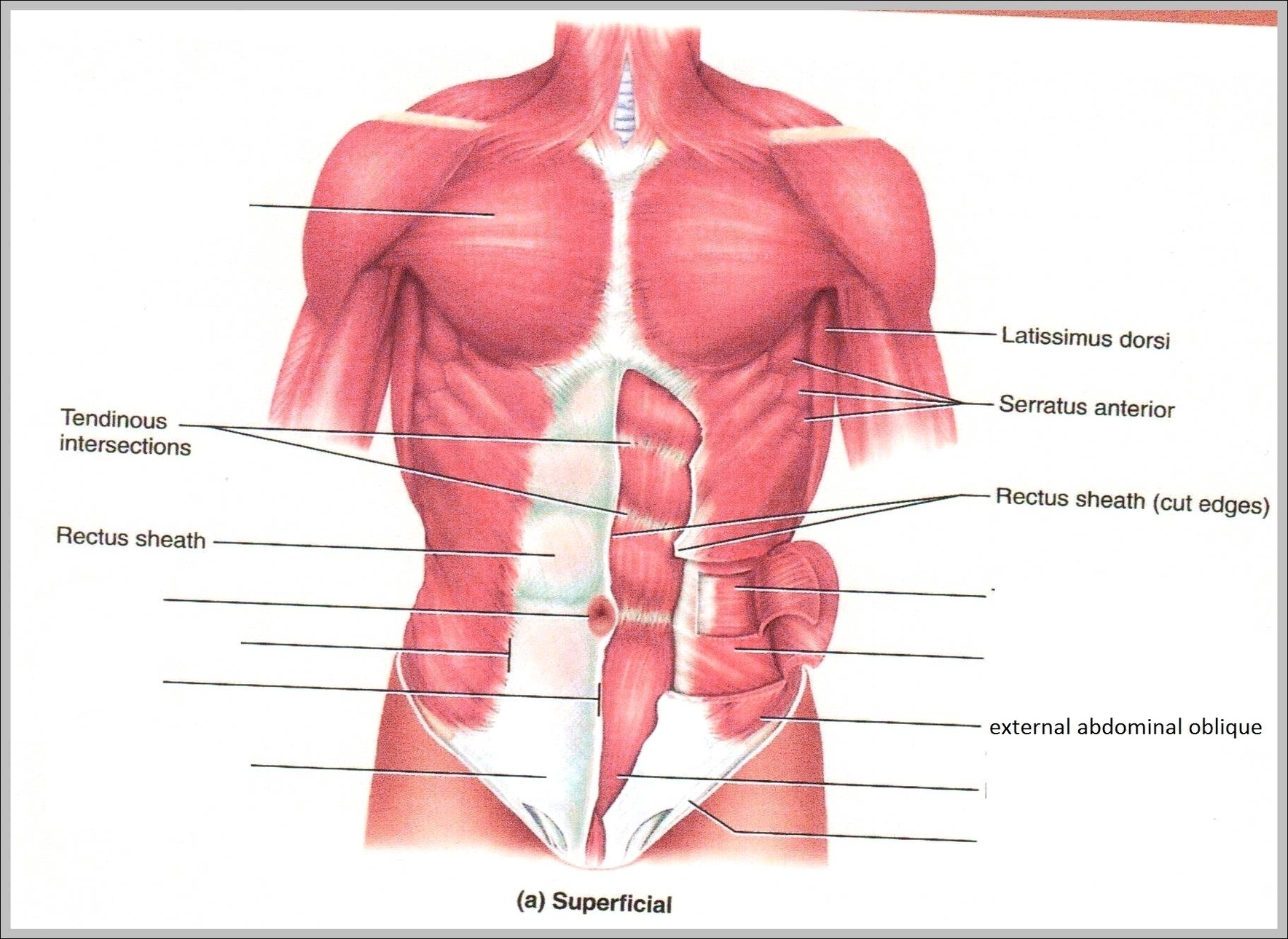
Muscles Of The Back And Neck
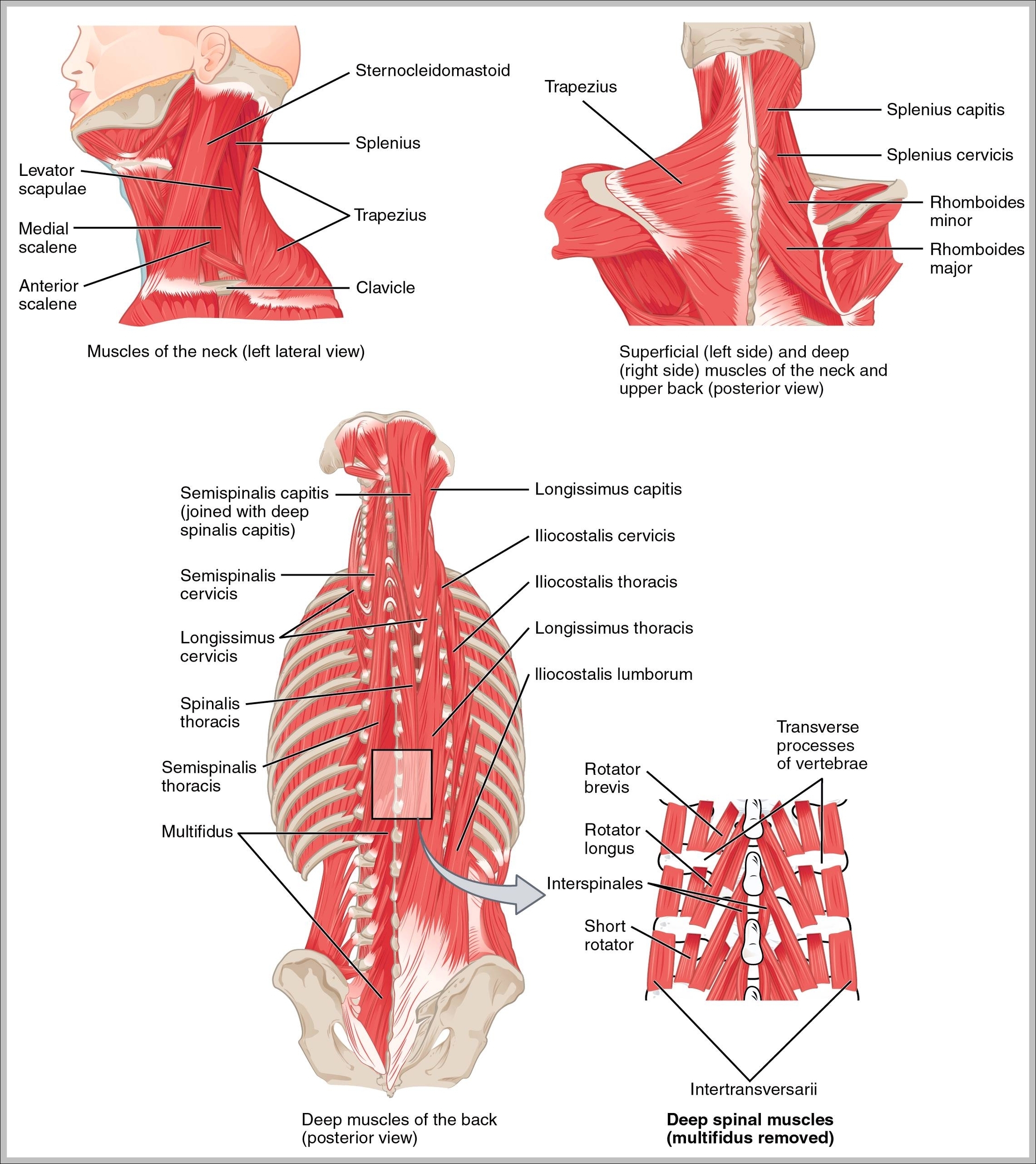
Muscles Of The Back And Neck: The muscles of the back and neck, including the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and sternocleidomastoid, are crucial for posture, head movement, and upper body stability. They also support the spine and assist in actions like View Diagram Muscles Of The Back And Neck