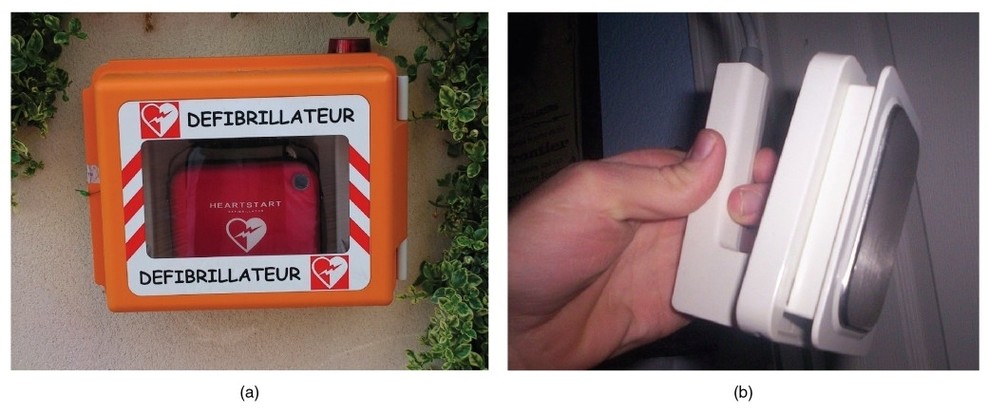
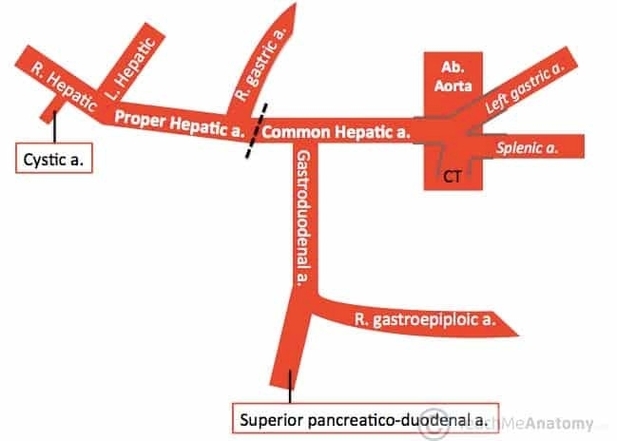
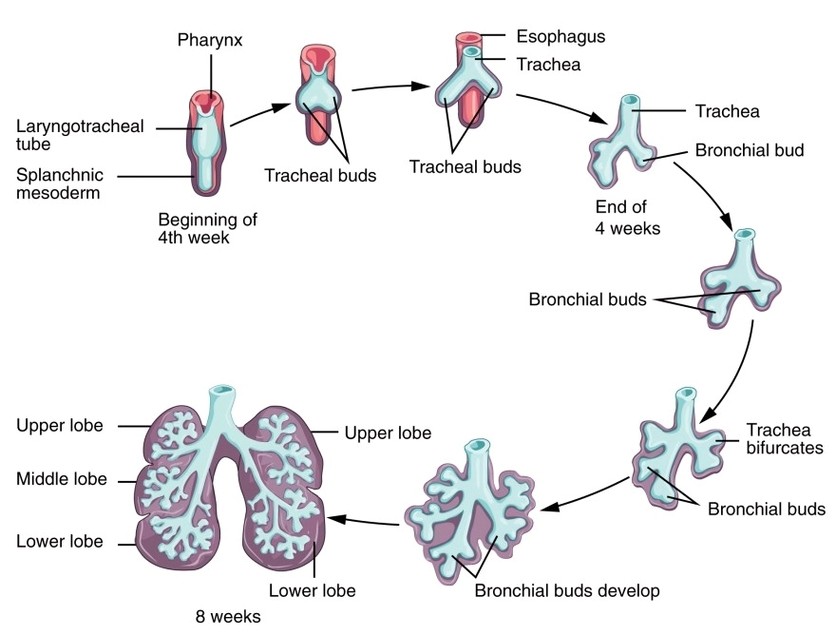
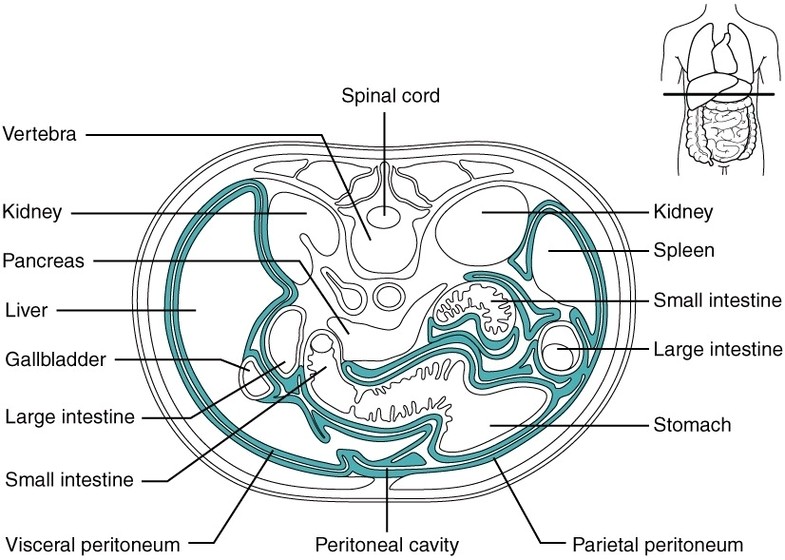
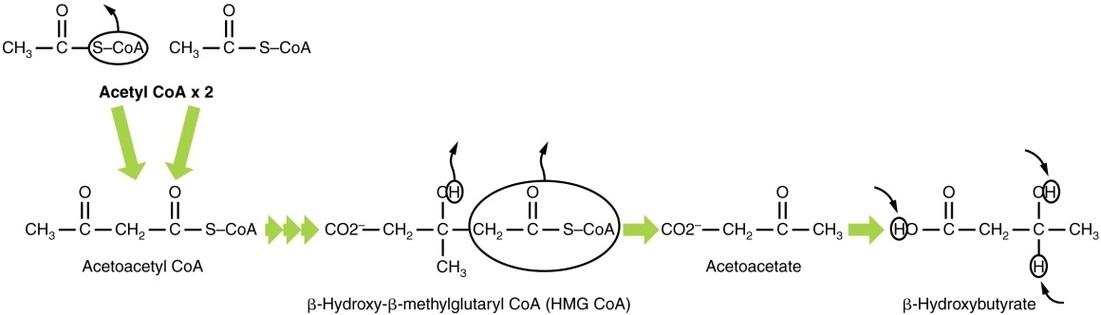
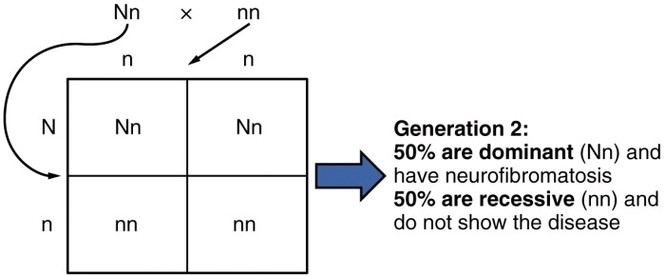
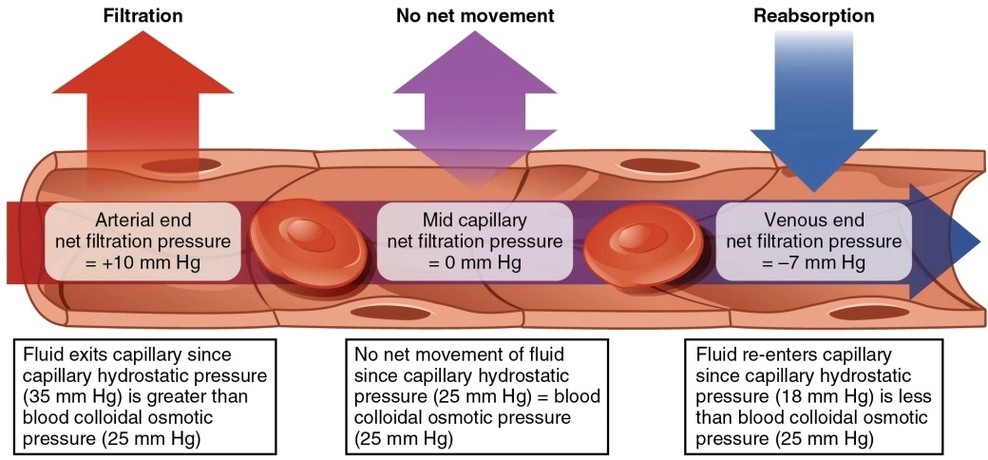
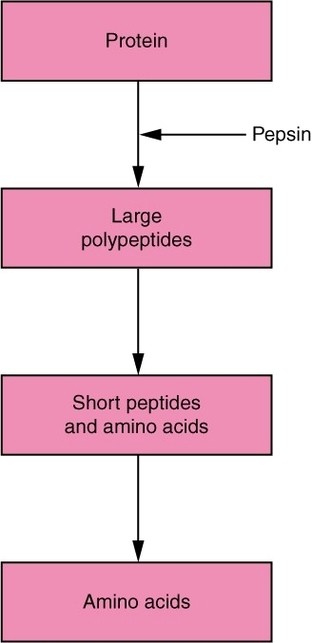
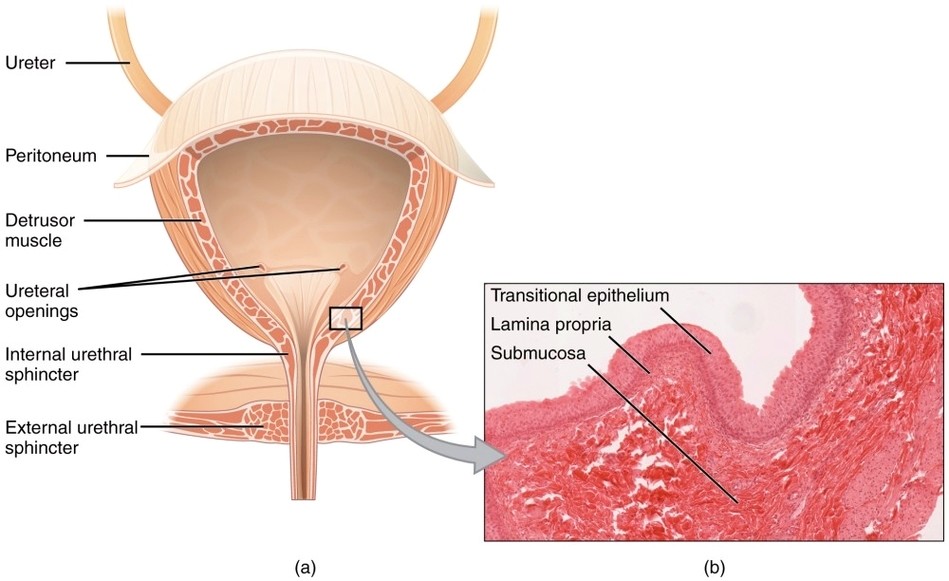
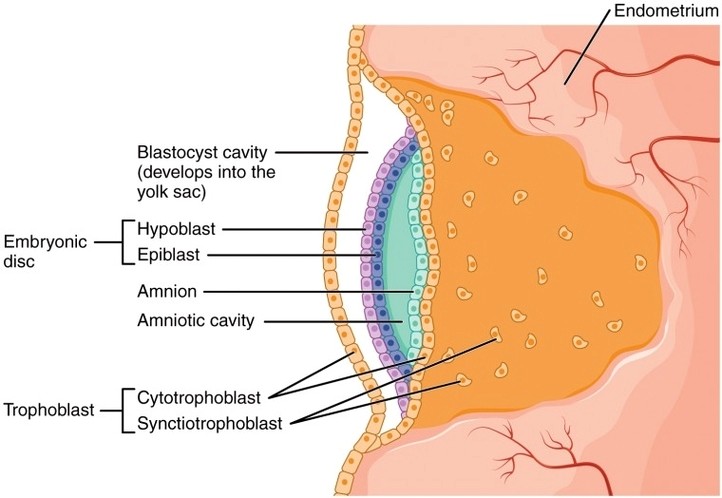
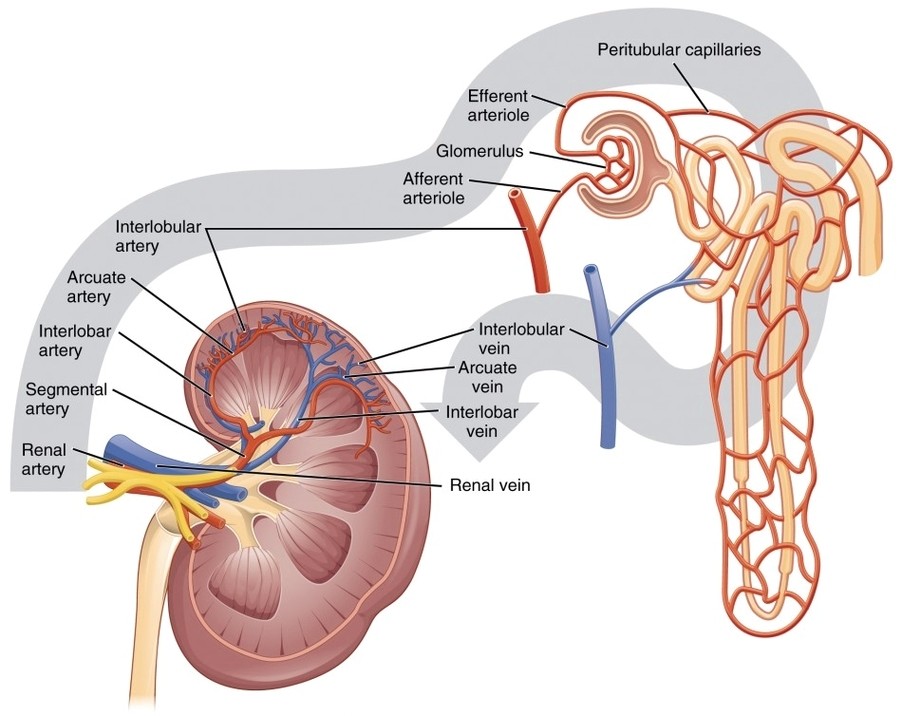
Parts of the Parietal Pleura
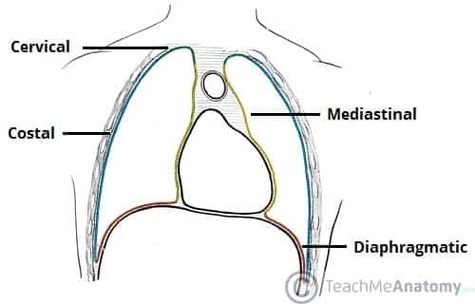
The parietal pleura consists of four continuous regionscostal, diaphragmatic, mediastinal, and cervical pleuraeach lining a different part of the thoracic cavity. The costal pleura covers the inner surfaces of the ribs and intercostal spaces, while the diaphragmatic pleura reflects over View Diagram Parts of the Parietal Pleura