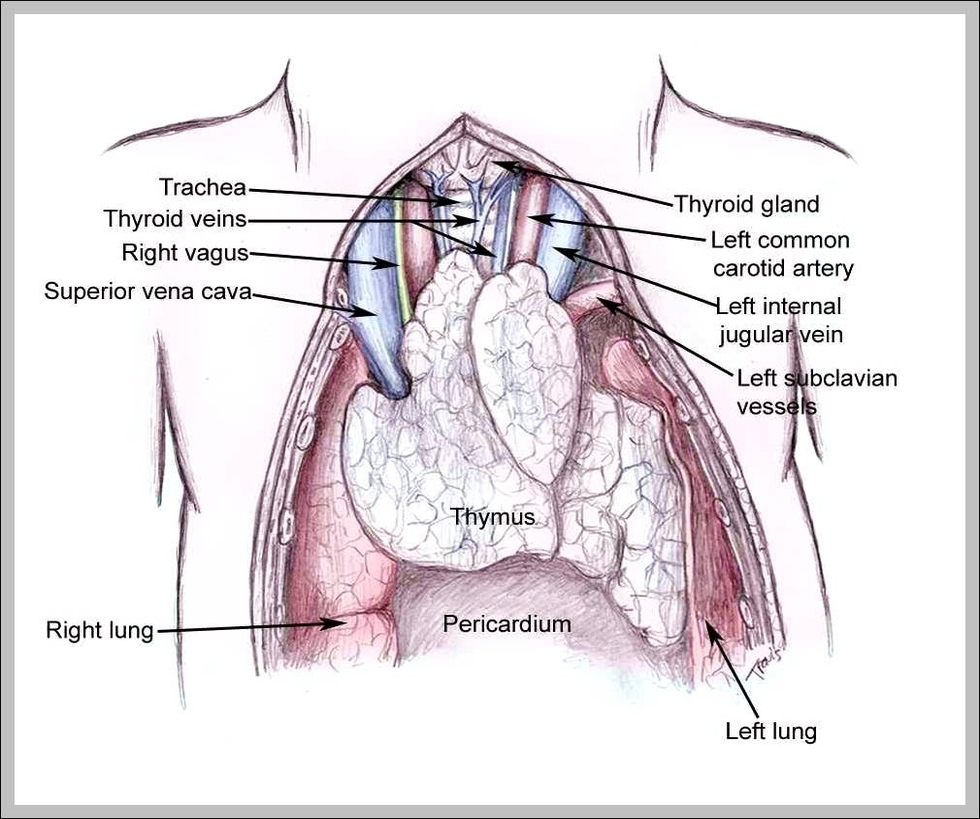
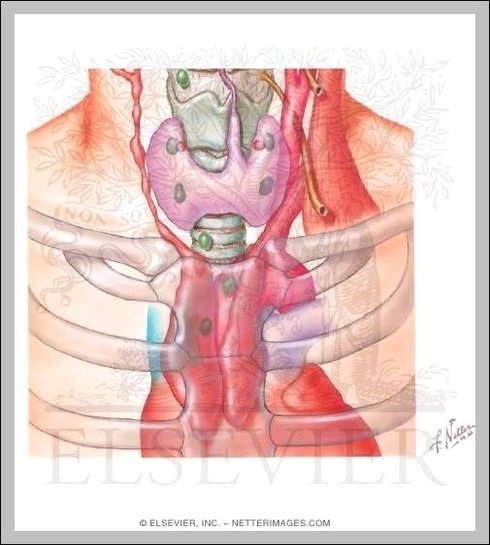
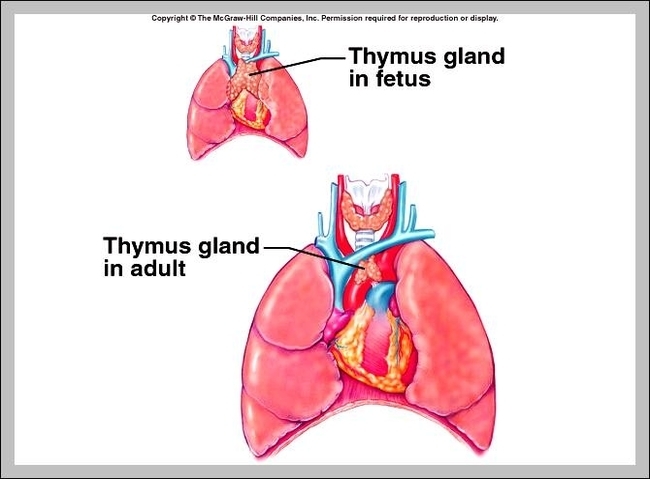
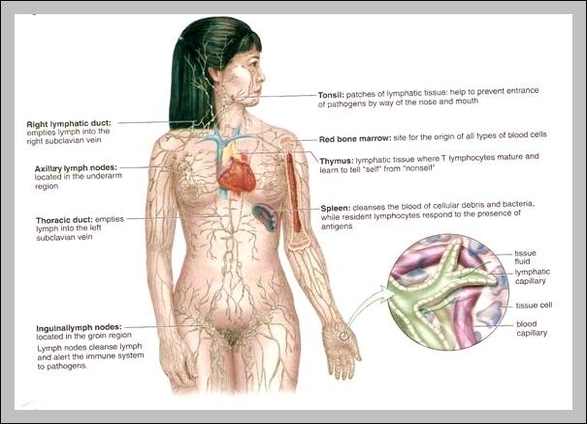
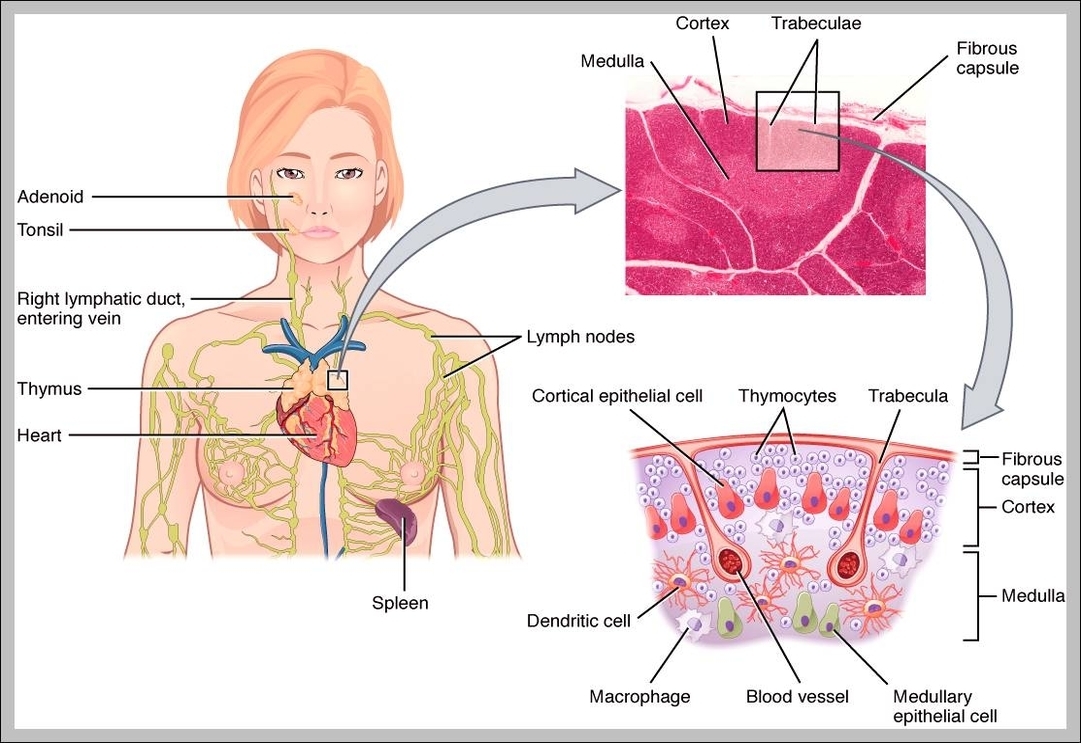
Role Of Thymus
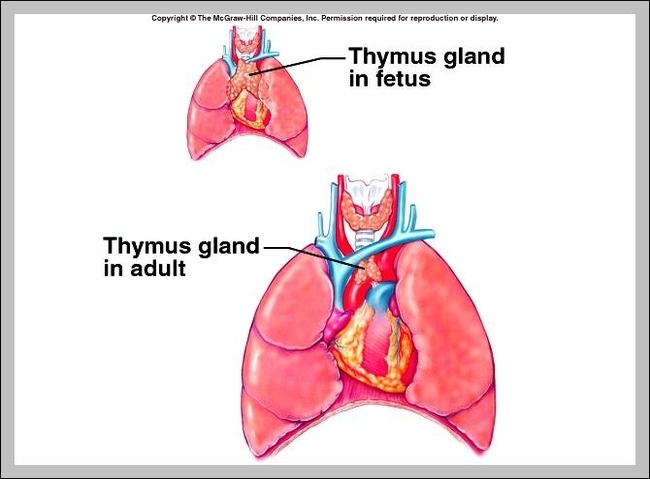
The main function of the thymus gland is to release thymosin hormone that will stimulate the maturation of T cells. All of our childhood, white blood cells or lymphocytes will come in contact with the thymus gland. The thymus is View Diagram Role Of Thymus