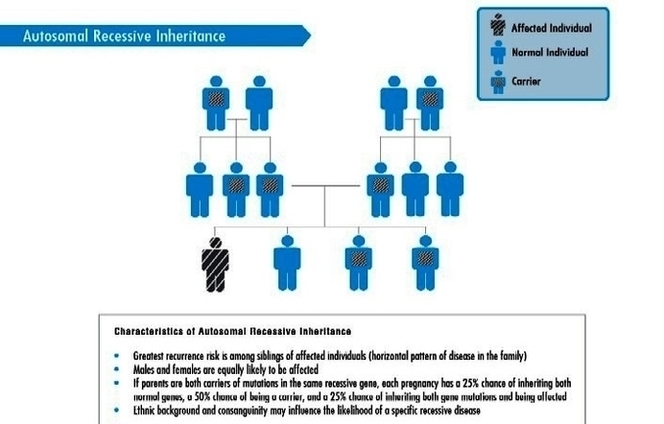
Autosomal recessive is a pattern of inheritance characteristic of some genetic disorders. “Autosomal” means that the gene in question is located on one of the numbered, or non-sex, chromosomes. Recessive Inheritance Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Recessive Inheritance Image and explains the details of Recessive Inheritance Image.
Recessive Inheritance Image