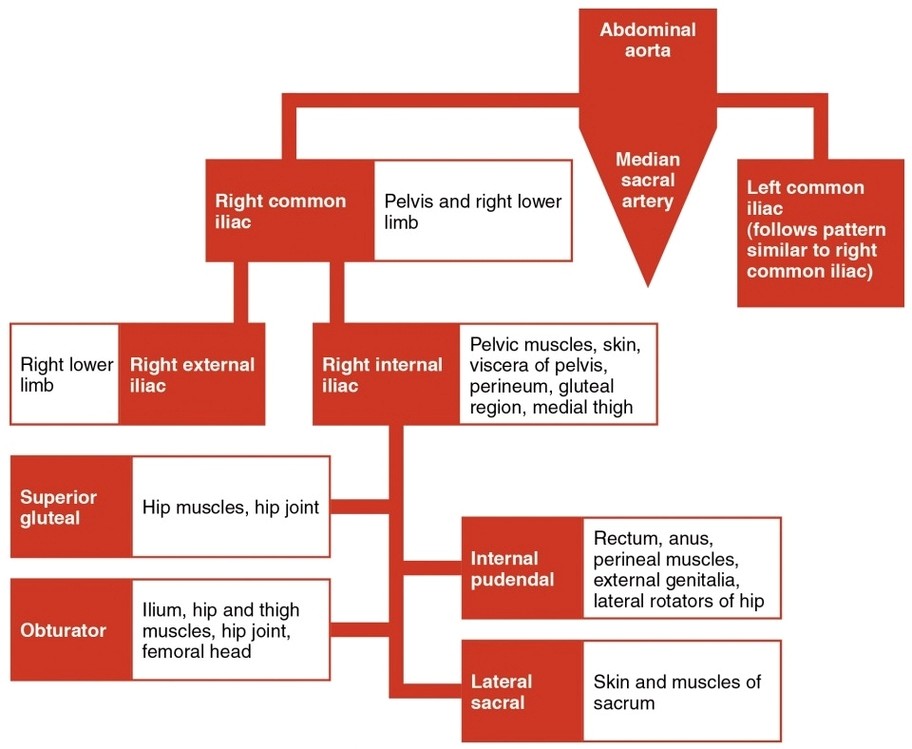
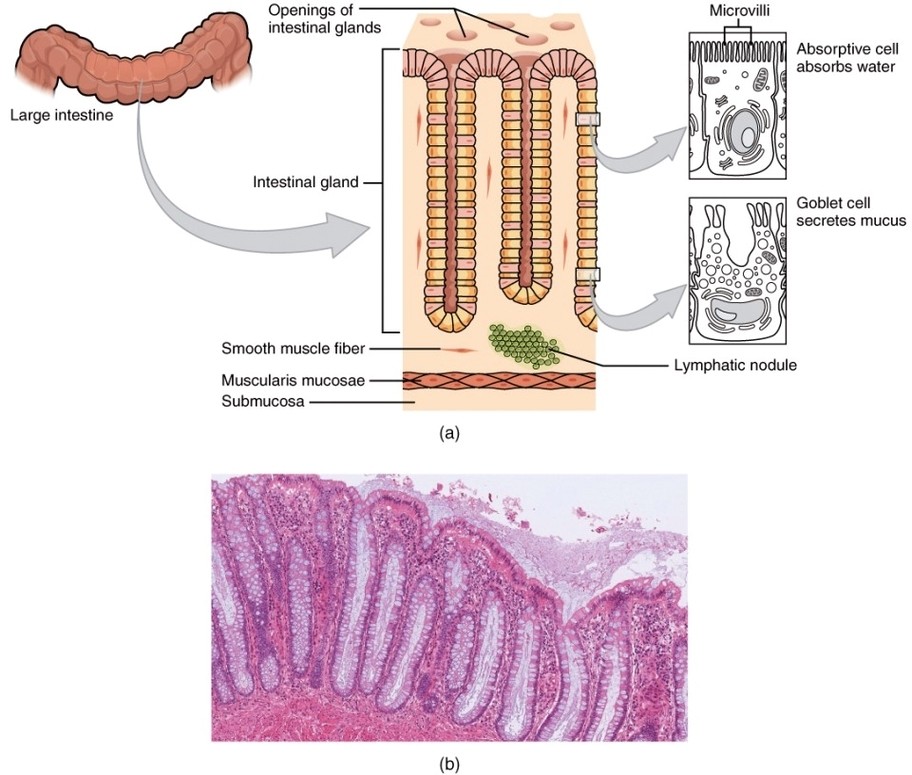
Category Archives: Anatomy
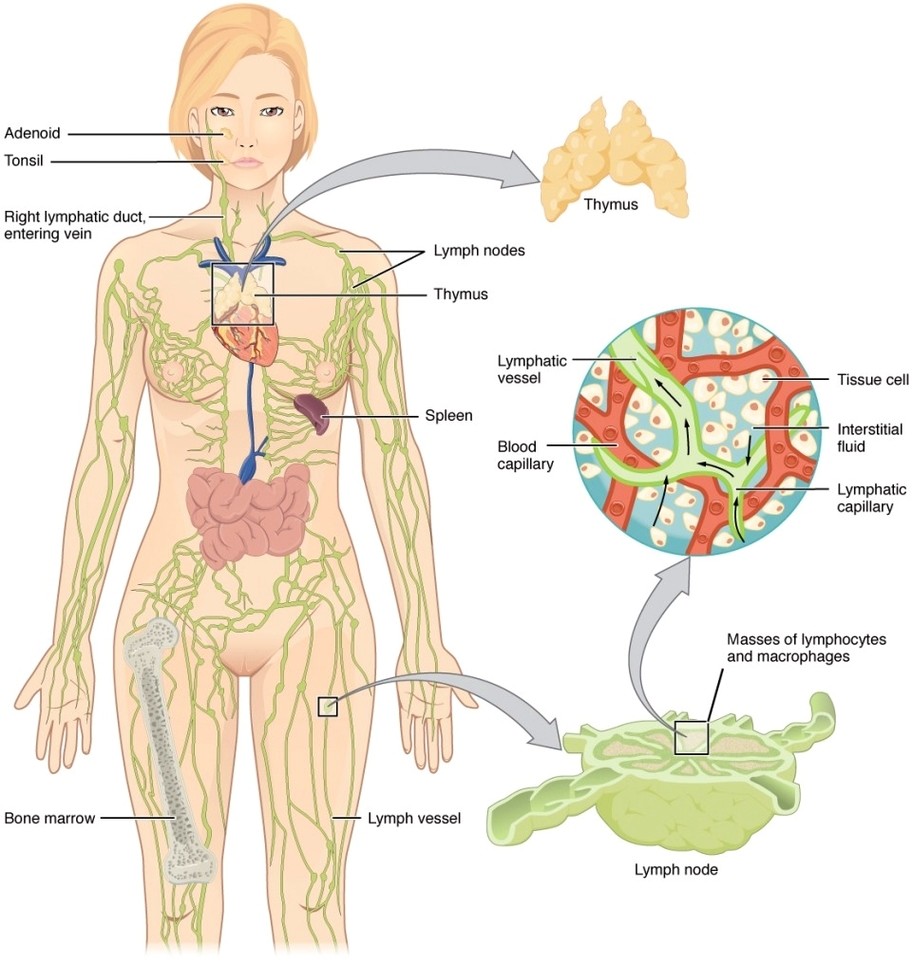
Anatomy of the Lymphatic System
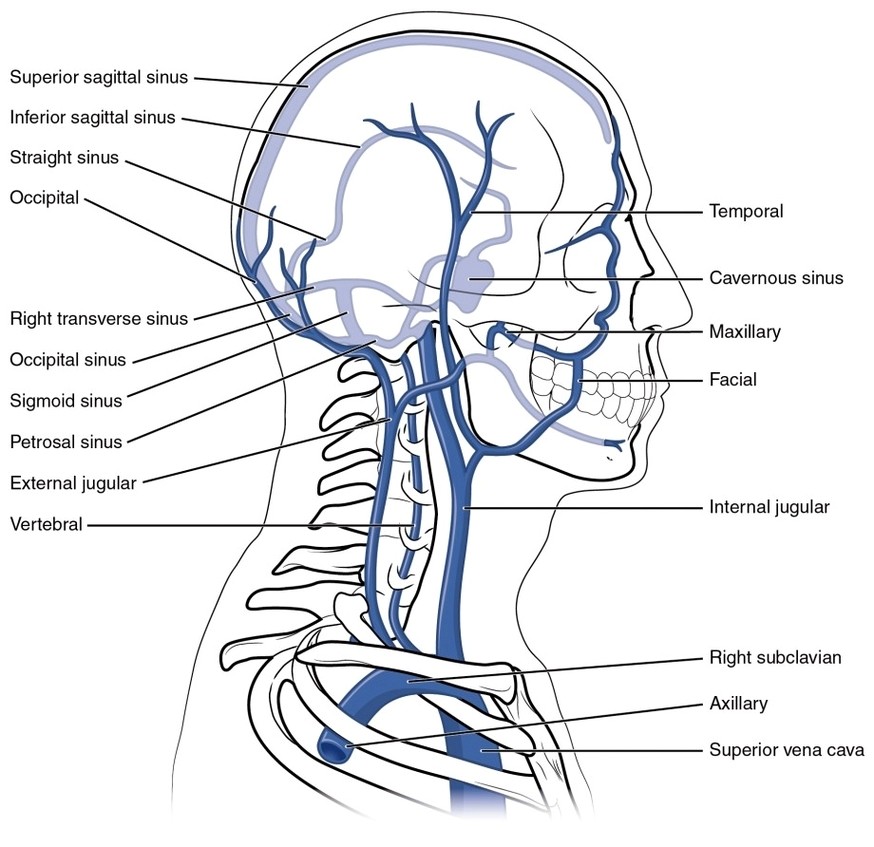
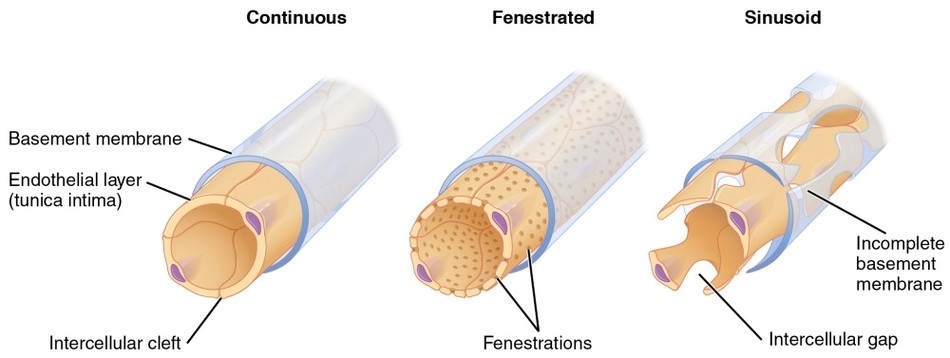
Head and Neck Veins
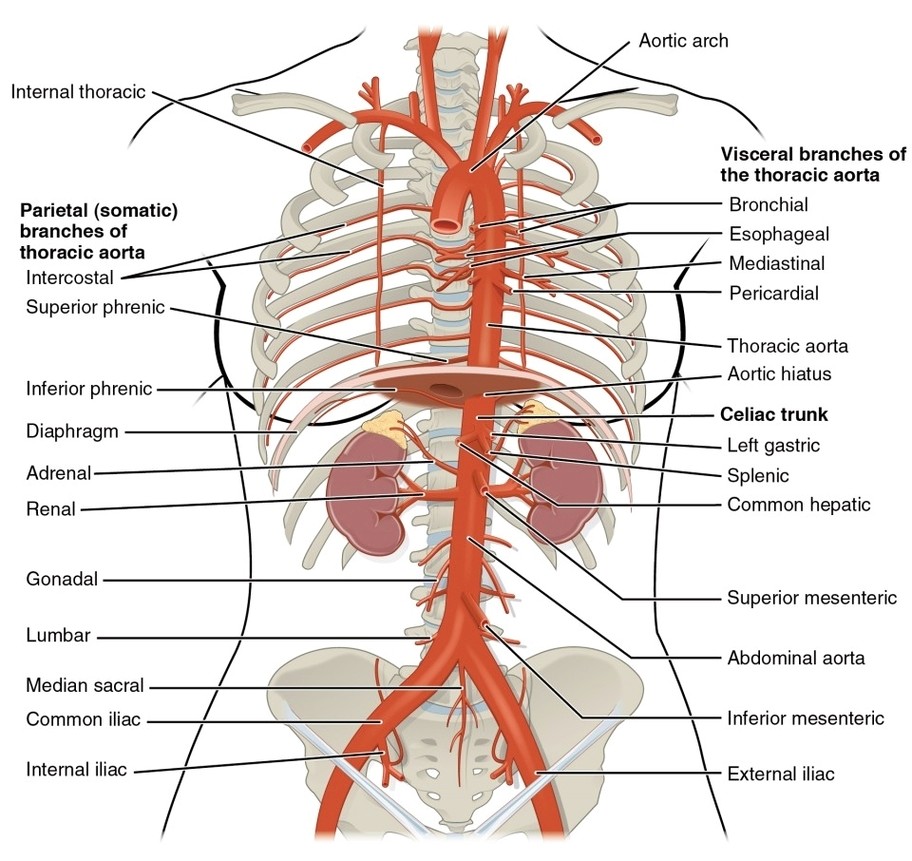
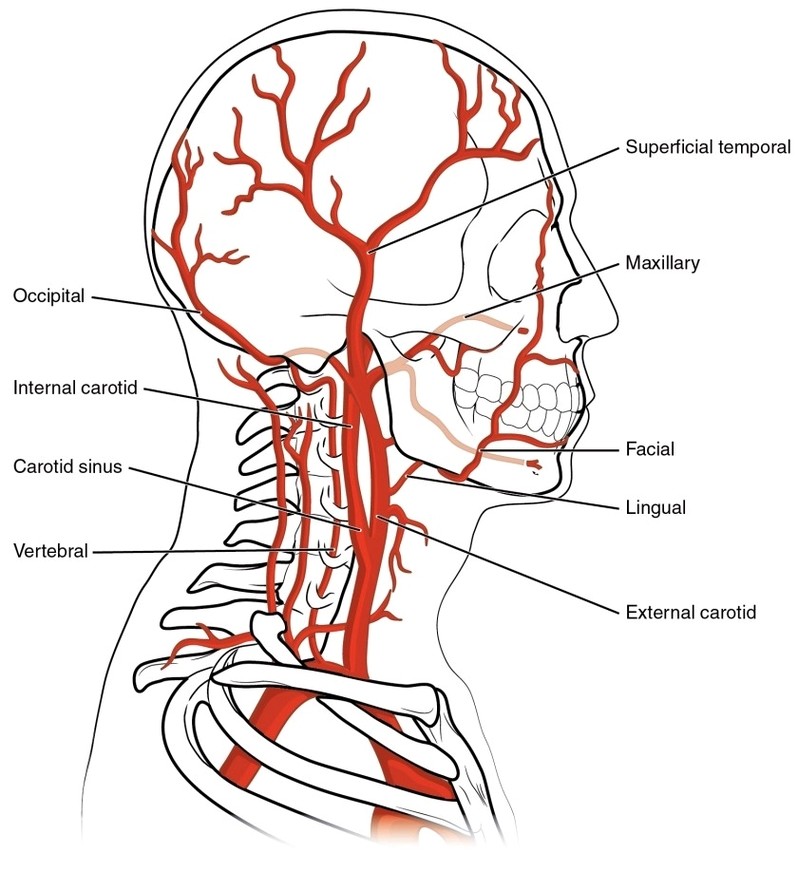
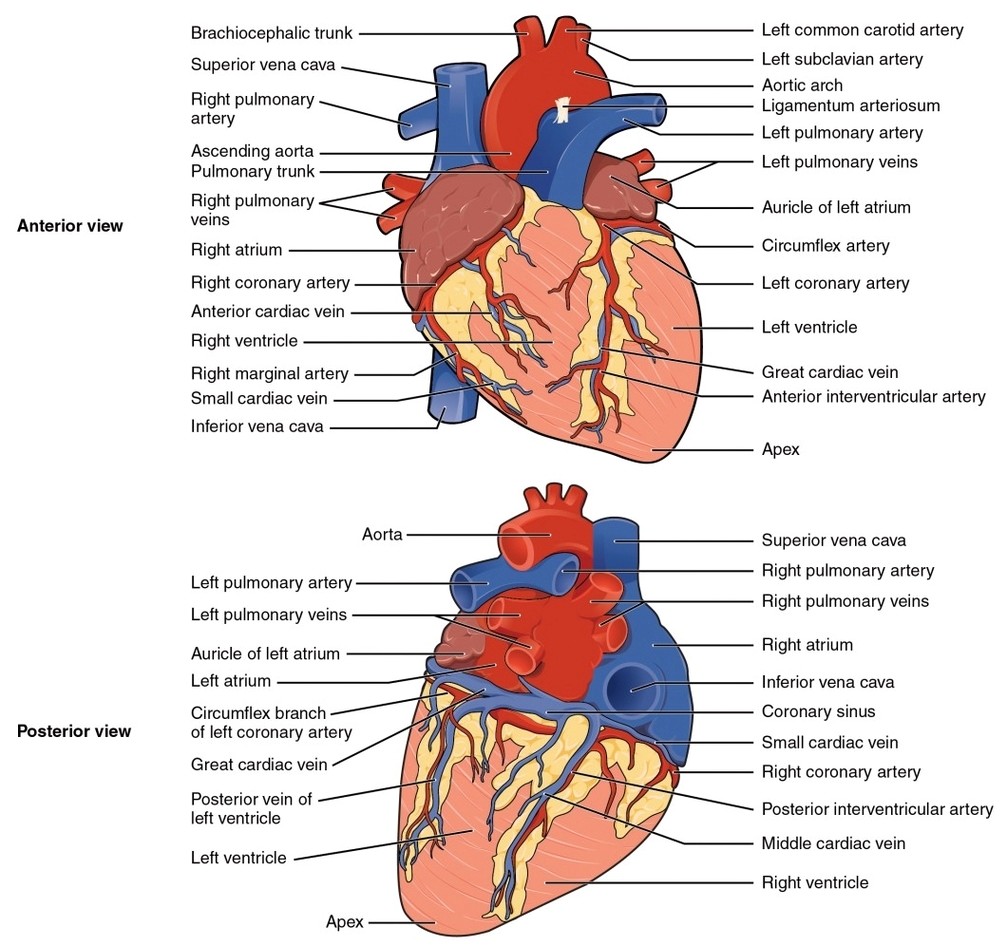
Common Carotid Artery
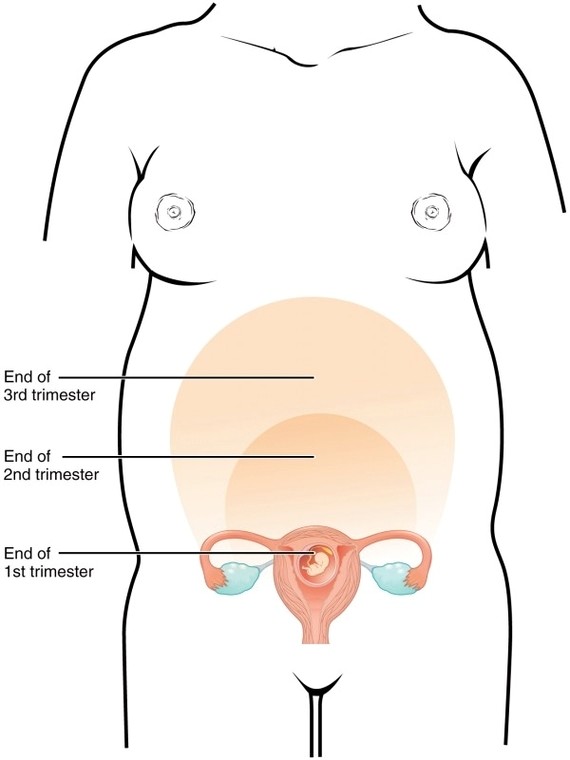
Size of Uterus Throughout Pregnancy
Digestion of Proteins Physiology
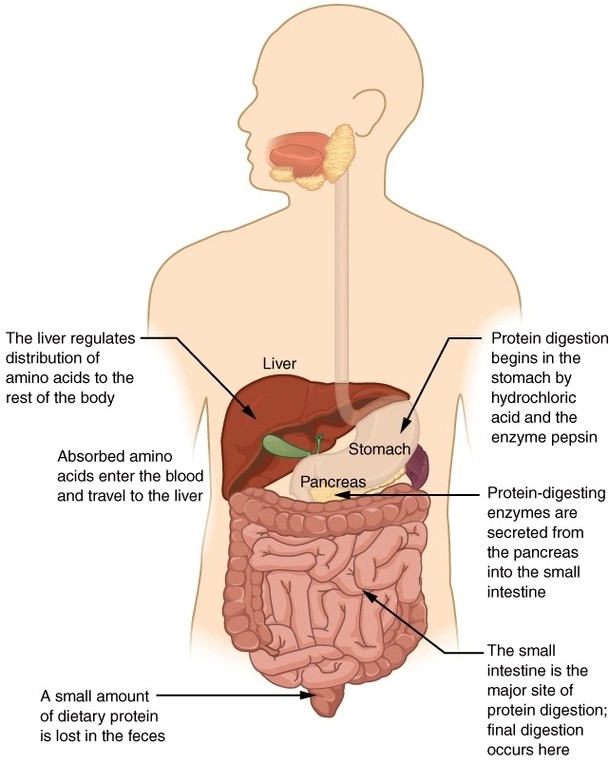
Digestion of Proteins Physiology: Protein digestion begins in the stomach, where the enzyme pepsin breaks down complex proteins into smaller peptides. This process continues in the small intestine, where pancreatic enzymes like trypsin and chymotrypsin further degrade peptides into amino View Diagram Digestion of Proteins Physiology
NEW-6-4-13

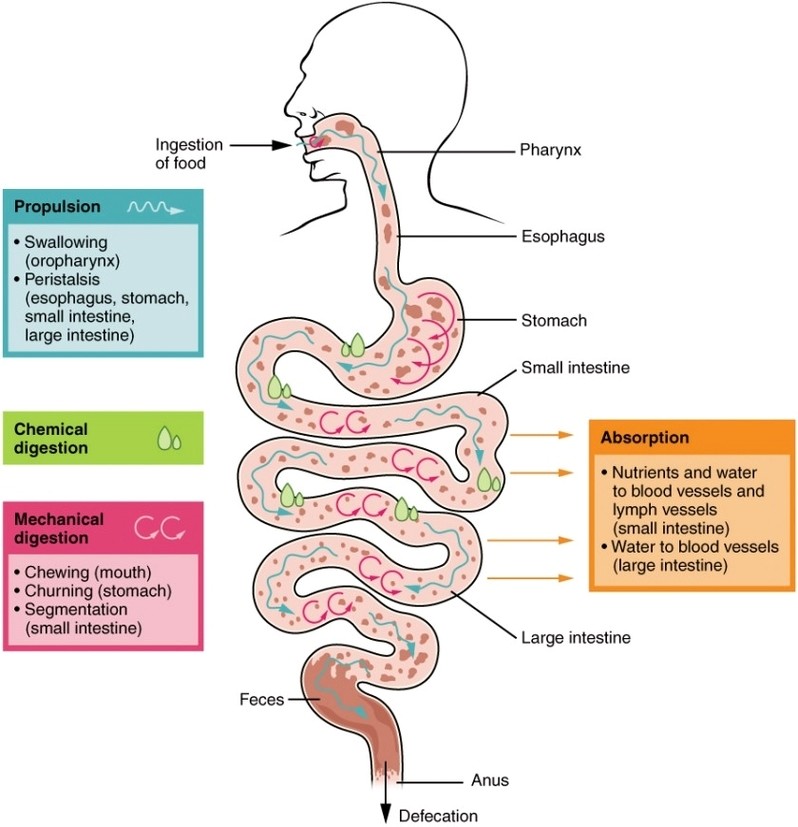
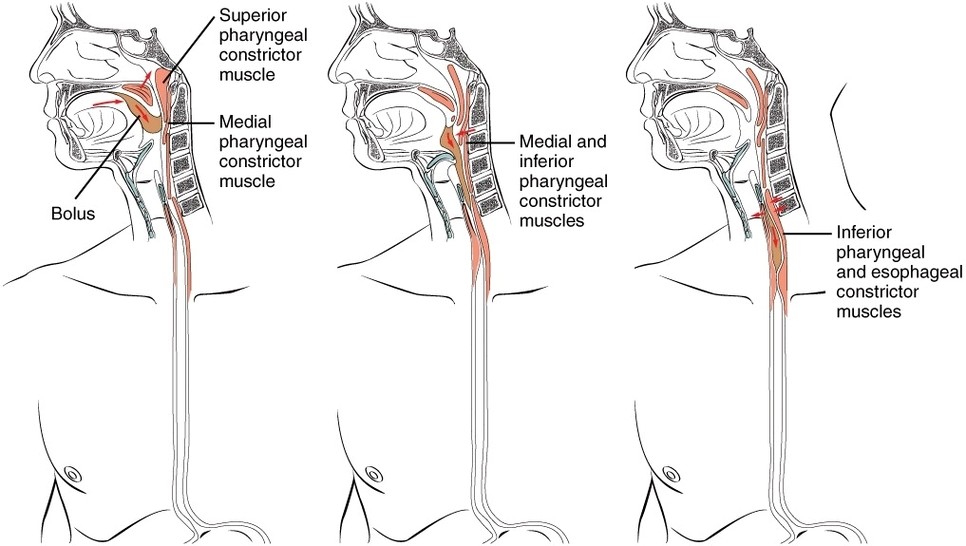
Digestive Process
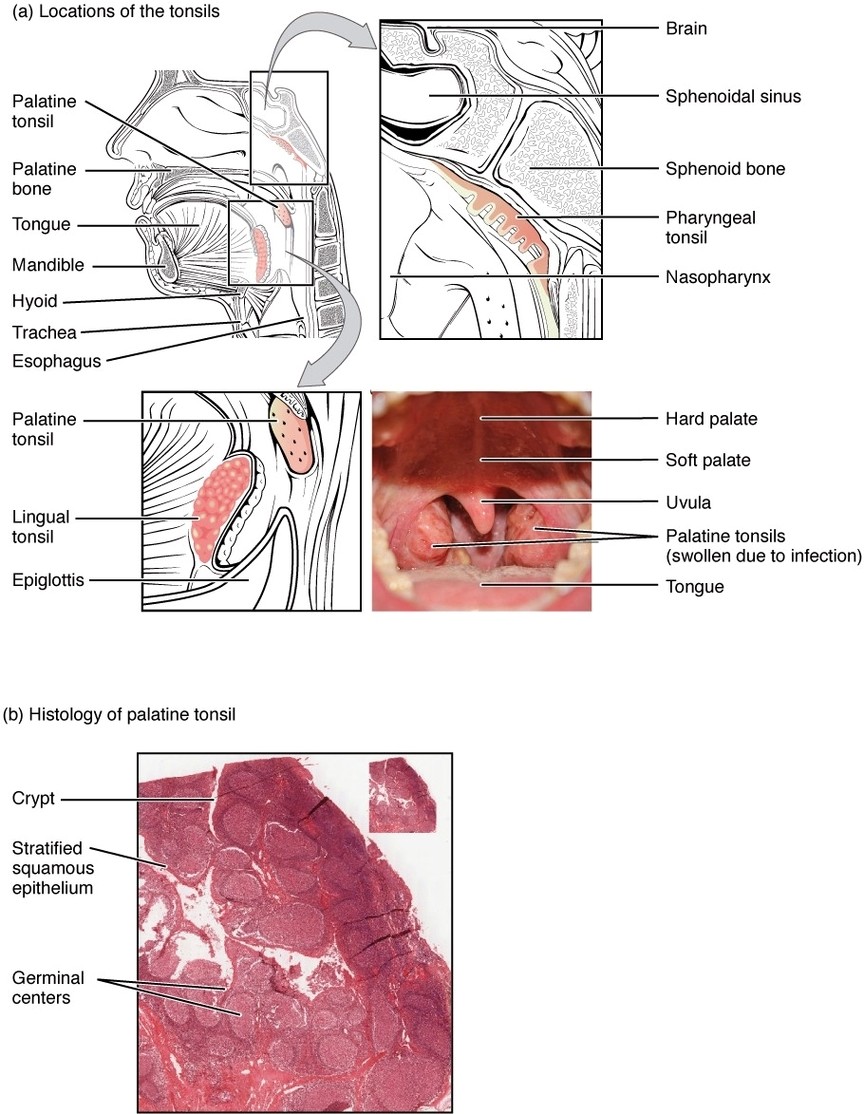
Location and History of Tonsils
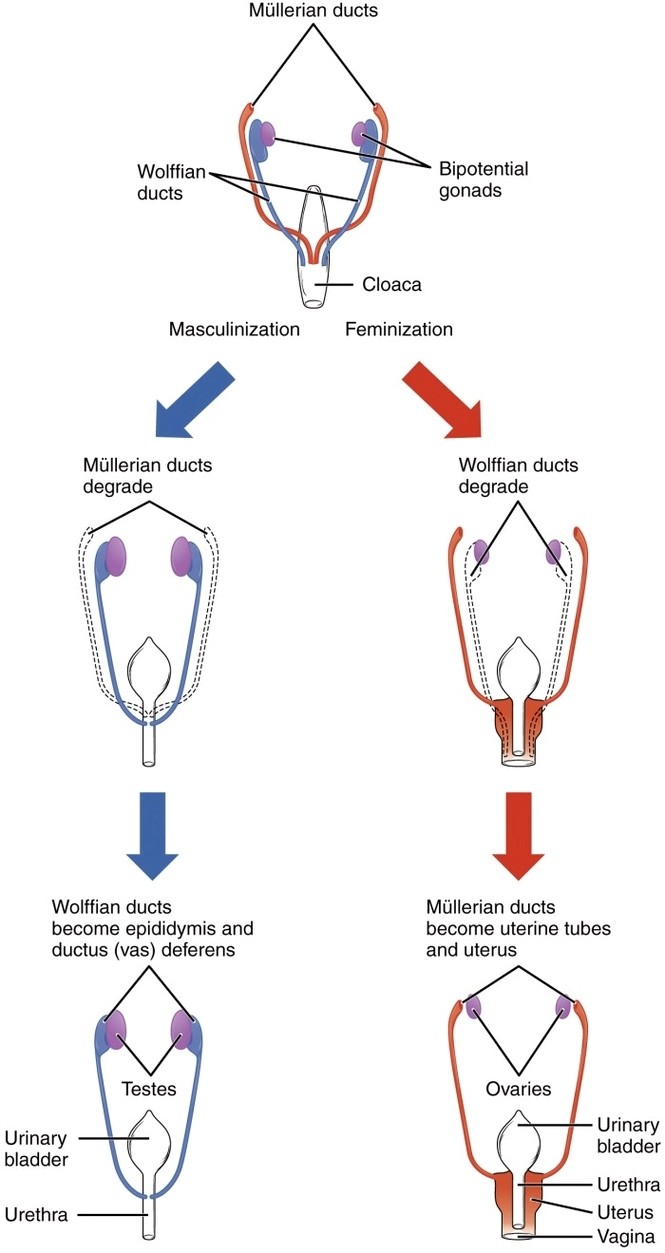
Sexual Differentation
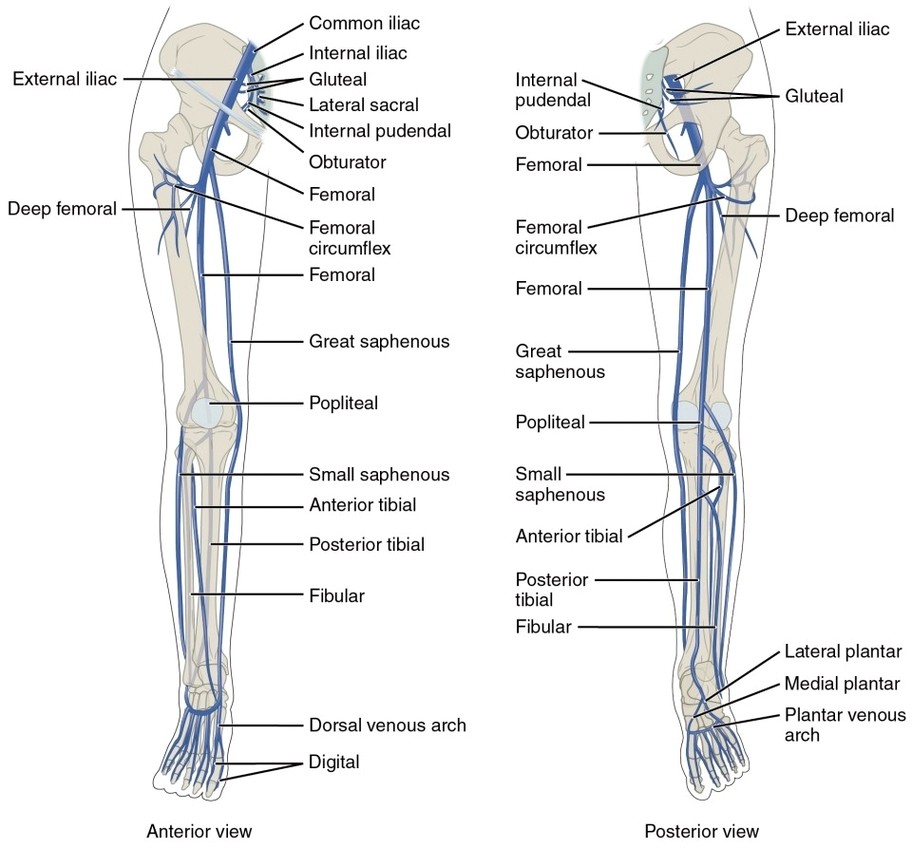
Lower Limb Veins Anterior Posterior
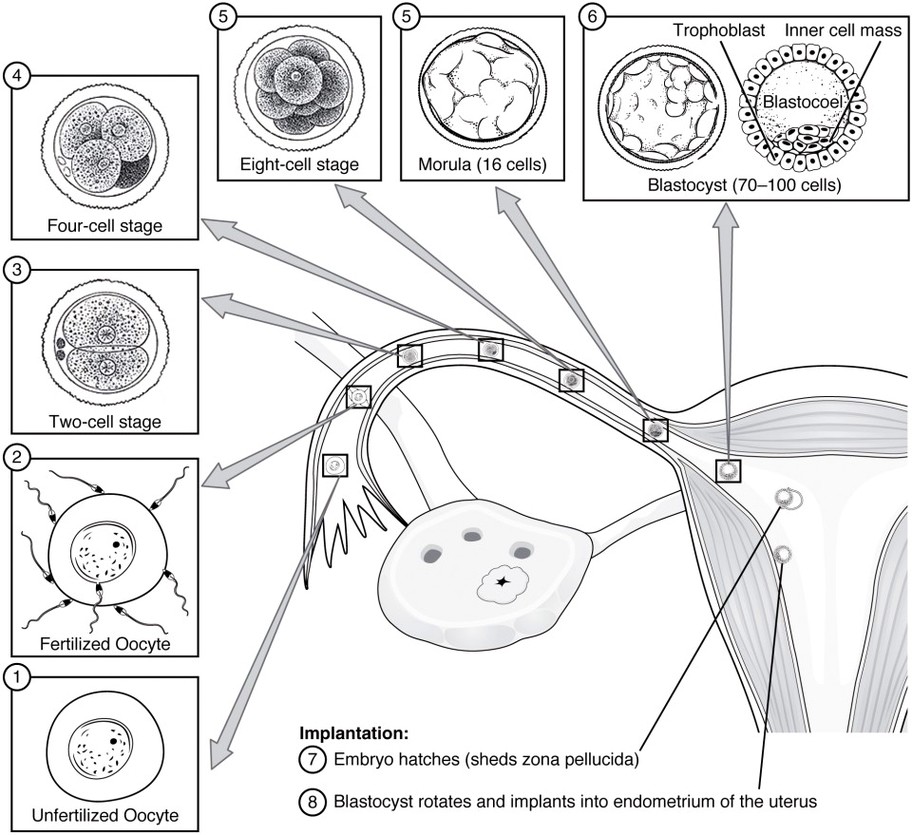
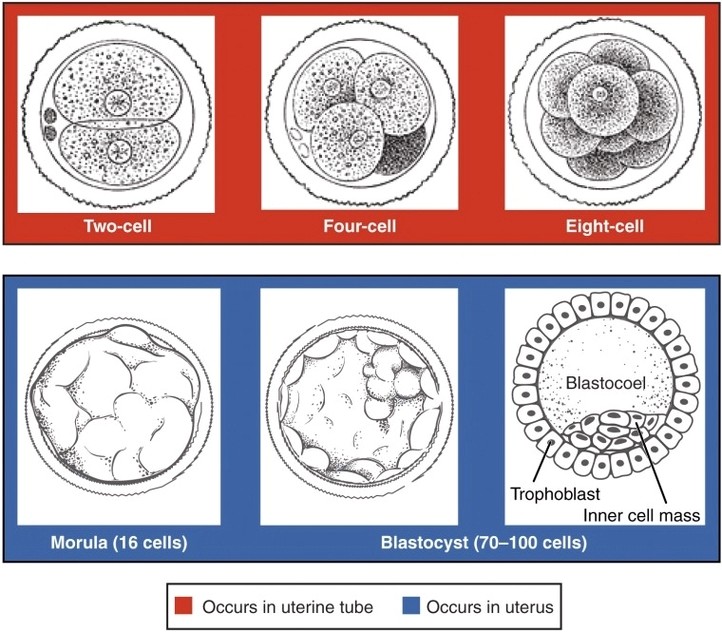
Preembryonic Development
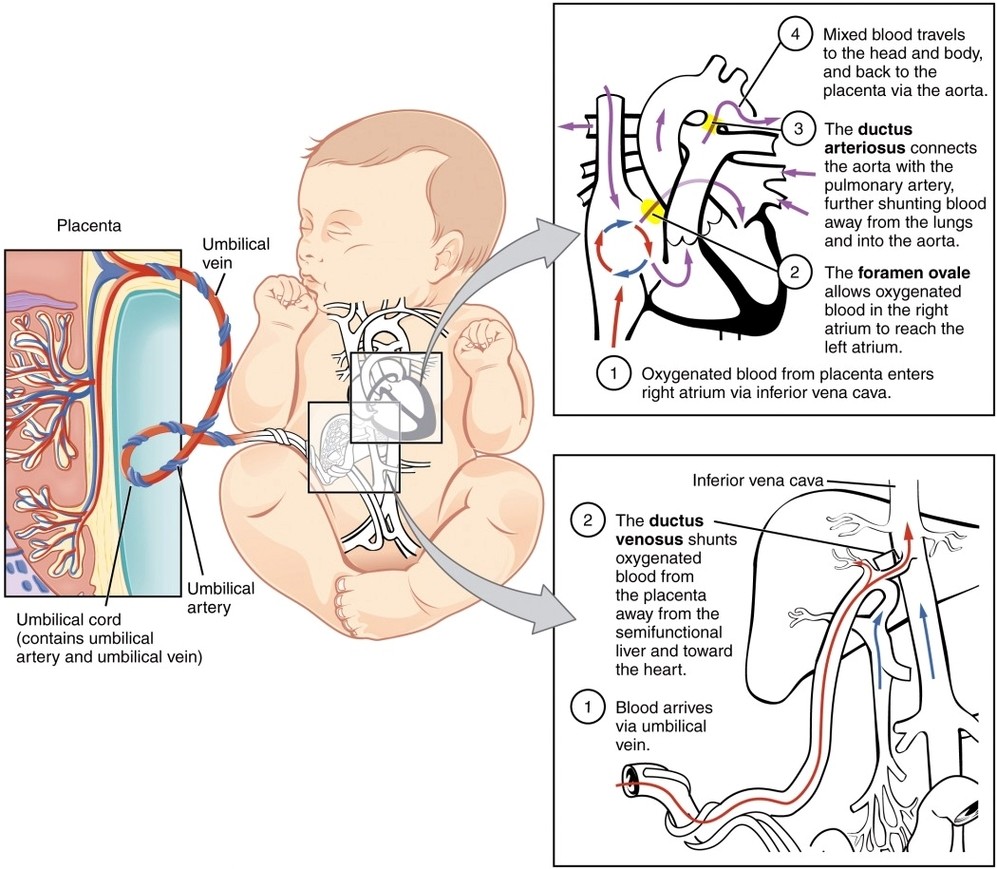
Fetal Circulatory System
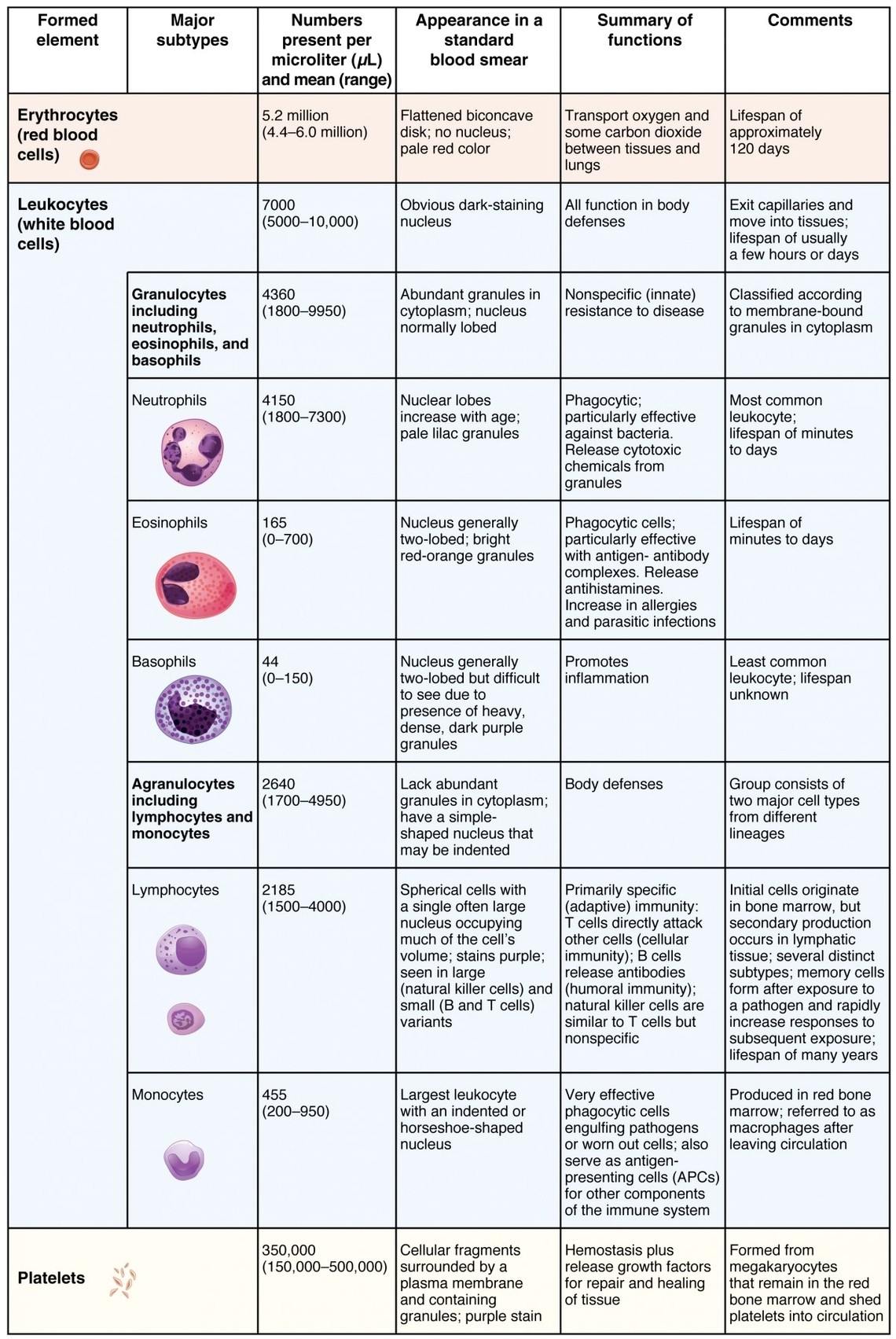
Table-19-3-1