Category Archives: Health
X Ray Generation Imagine
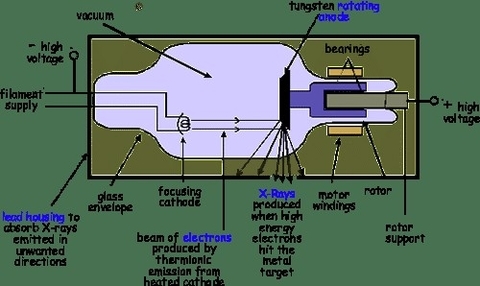
X-ray generation involves producing electromagnetic radiation through acceleration of electrons onto a target anode, creating photons that penetrate tissues and create radiographic images. Knowledge of X-ray physics is essential for radiologists, technicians, and medical students in imaging diagnostics, safety protocols, View Diagram X Ray Generation Imagine
Muscles Innervated by the Accessory Nerve

Muscles innervated by the accessory nerve include the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius. The nerve provides motor control, facilitating head rotation, shoulder elevation, and posture maintenance. Knowledge of accessory nerve anatomy is essential for surgeons, neurologists, and medical students in diagnosing nerve View Diagram Muscles Innervated by the Accessory Nerve
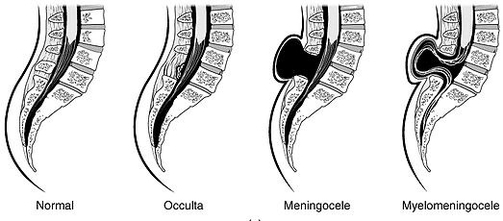
ASIA scale 571
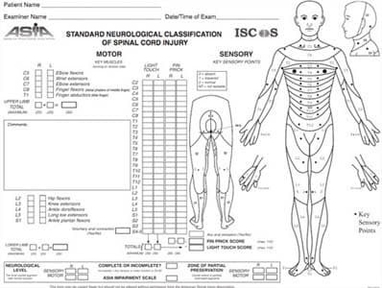
The ASIA scale 571 is used to classify the severity of spinal cord injuries based on motor and sensory function. It provides a standardized framework to determine whether injuries are complete or incomplete, guiding treatment and rehabilitation planning. Clinicians, therapists, View Diagram ASIA scale 571
Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Down and Out Position
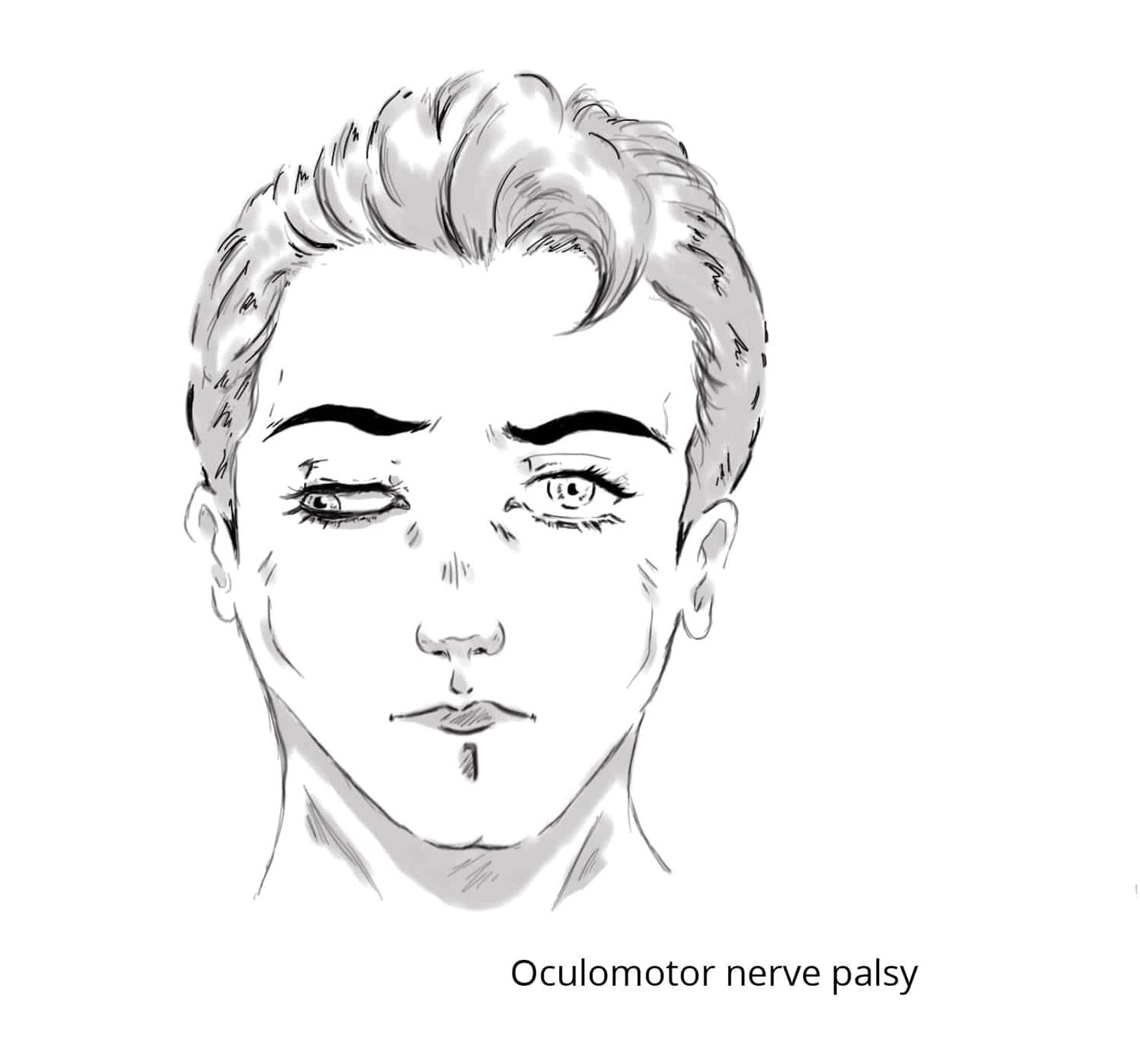
Oculomotor nerve palsy produces the classic down and out eye position because the muscles normally controlled by the oculomotor nerve lose their function, leaving only the lateral rectus and superior oblique muscles unopposed. As a result, the affected eye drifts View Diagram Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Down and Out Position
Ultrasound Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome on ultrasound typically shows enlarged ovaries with multiple small follicles arranged around the periphery, often described as a string of pearls. These follicles represent arrested development due to hormonal imbalance, particularly elevated androgens and disrupted ovulatory cycles. View Diagram Ultrasound Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Types of Synovial Joint
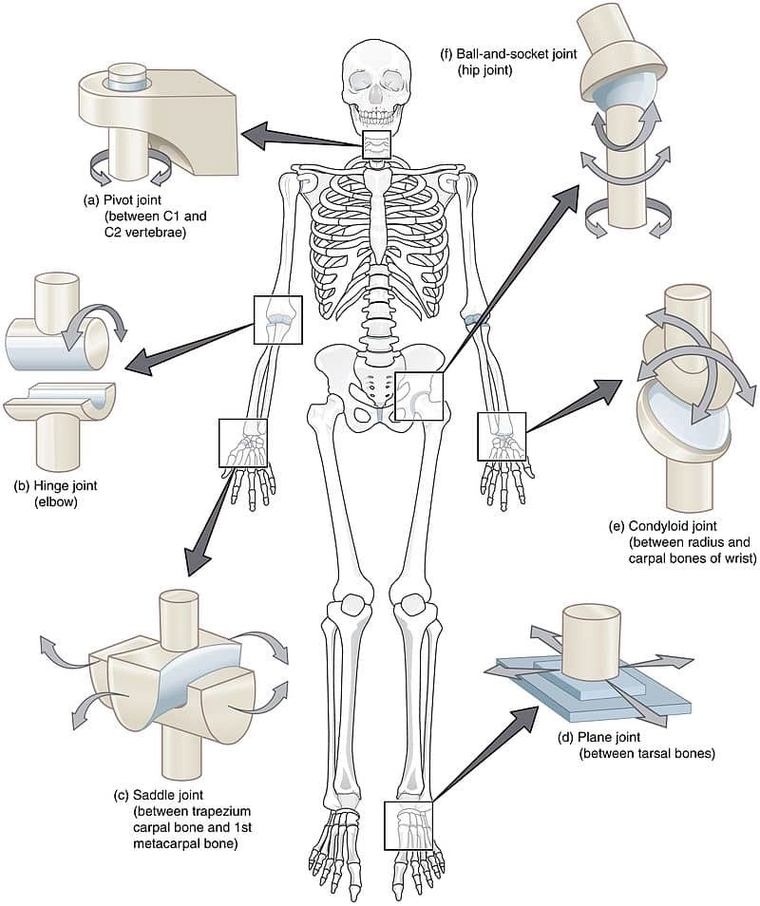
Synovial joints are highly mobile joints characterized by a synovial cavity filled with lubricating fluid, articular cartilage covering the joint surfaces, and a fibrous capsule that encloses the space. They come in several types, including hinge joints that permit flexion View Diagram Types of Synovial Joint