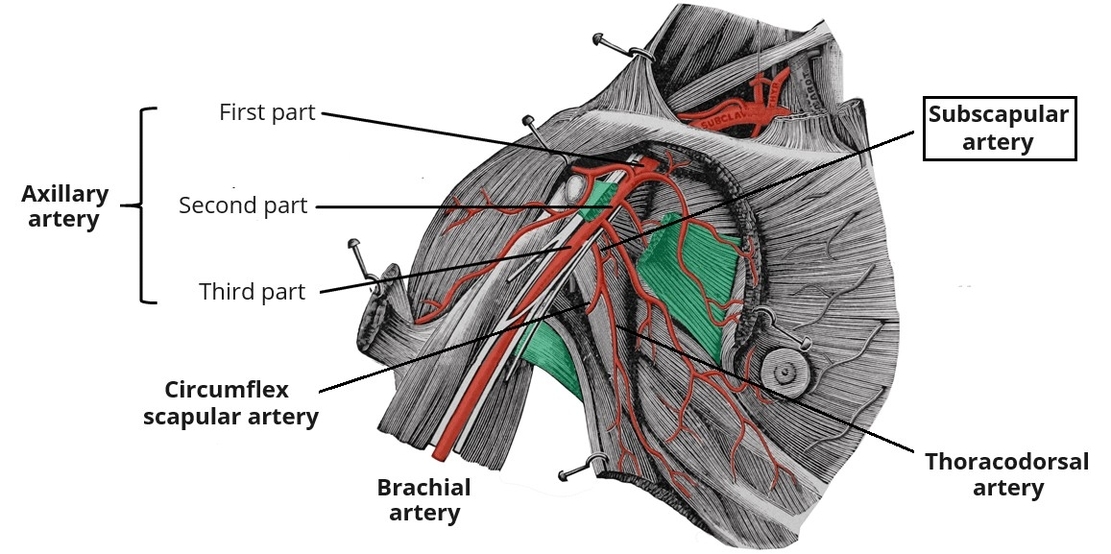
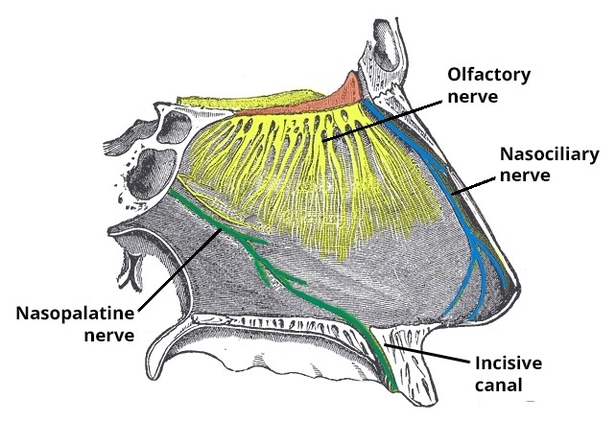
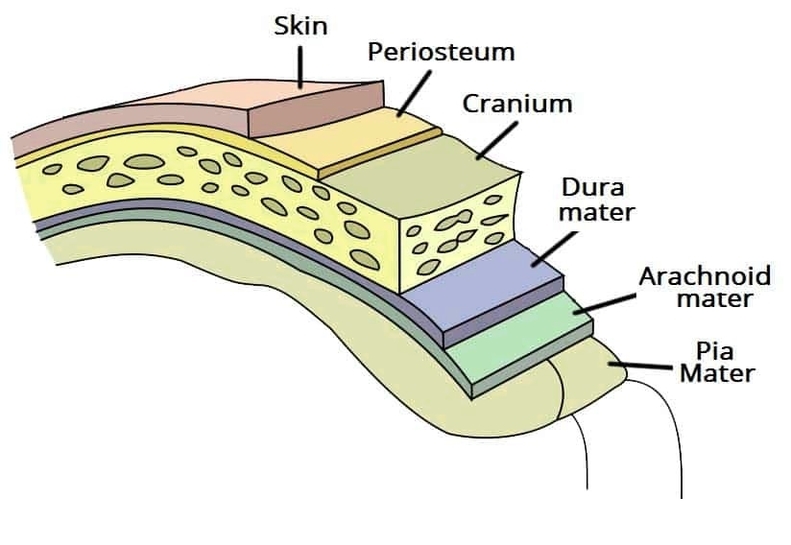
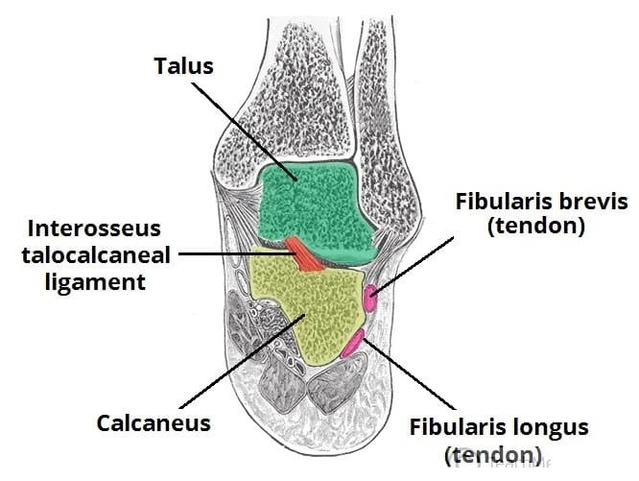
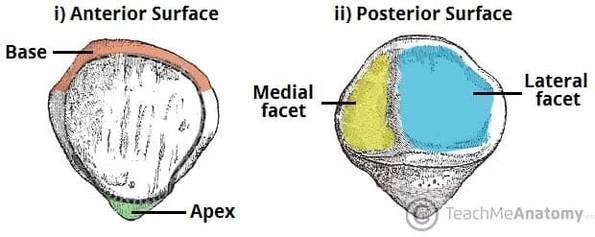
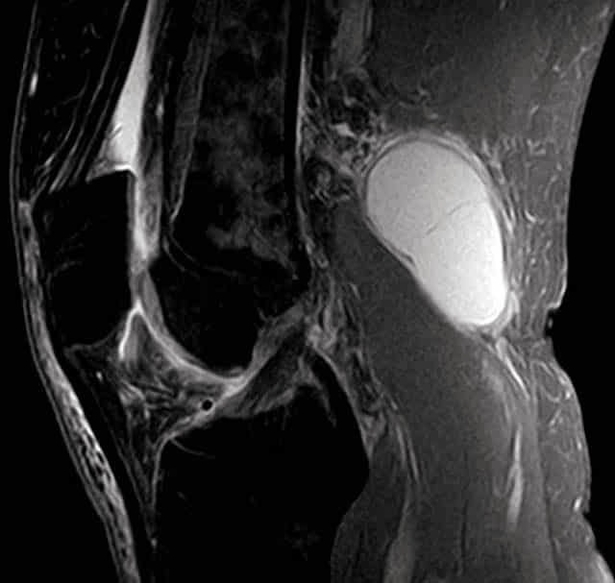
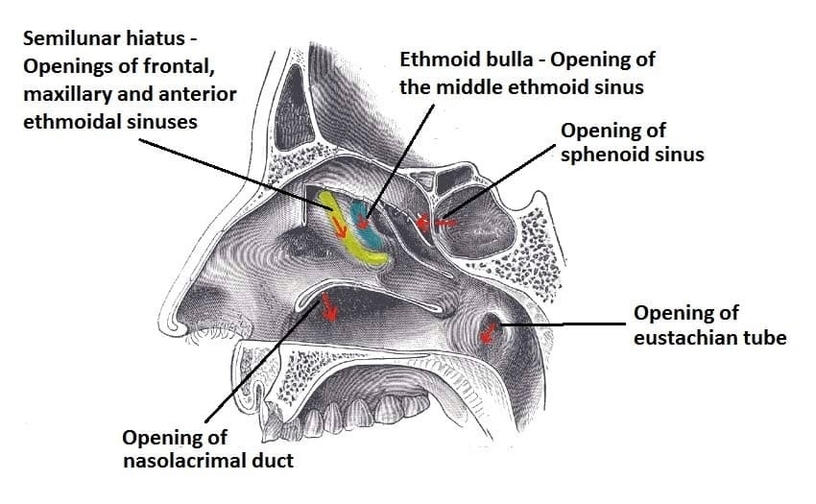
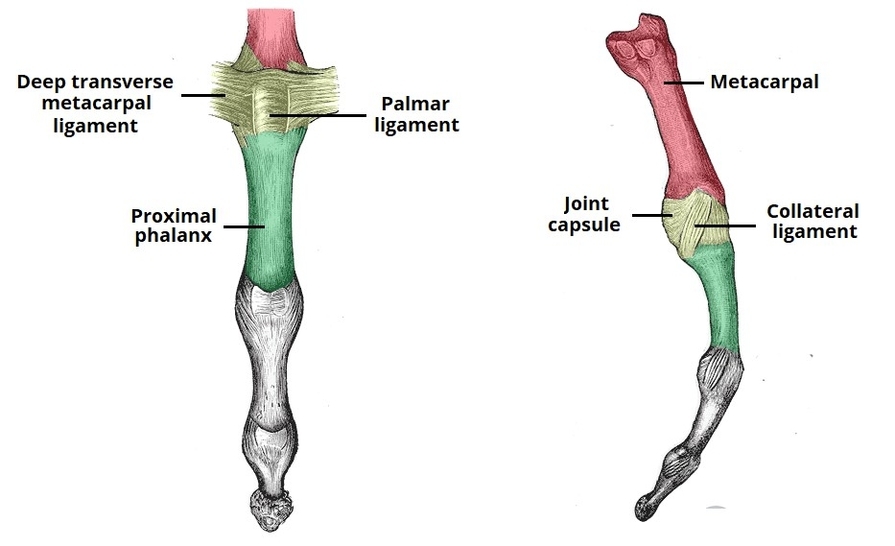
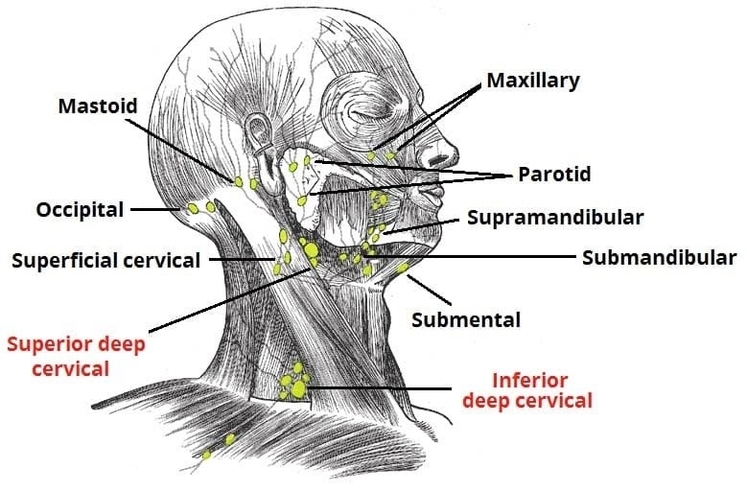
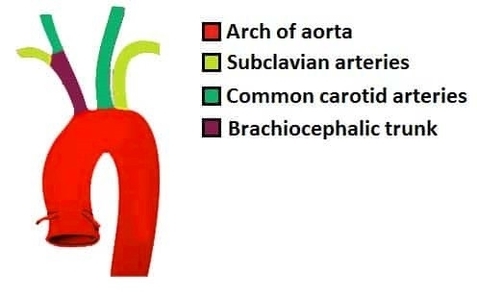
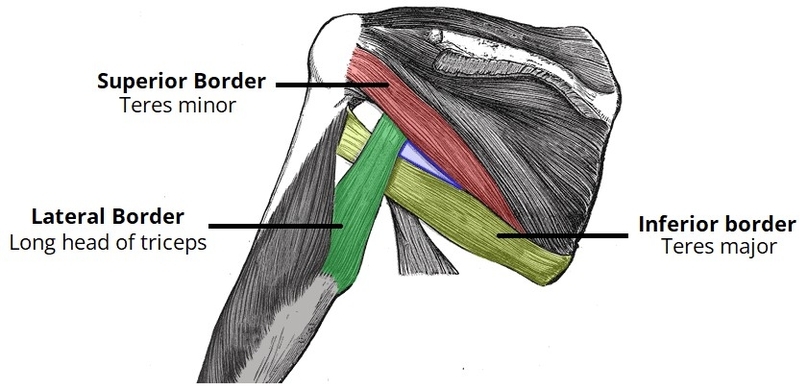
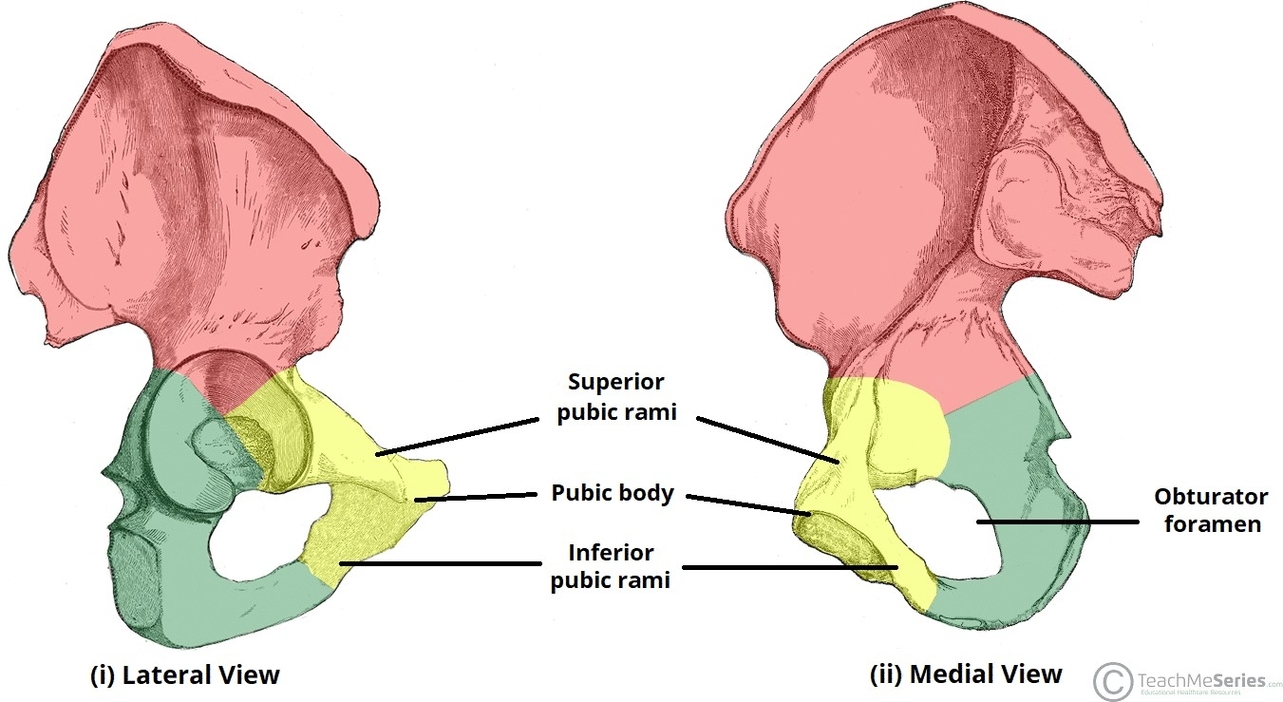
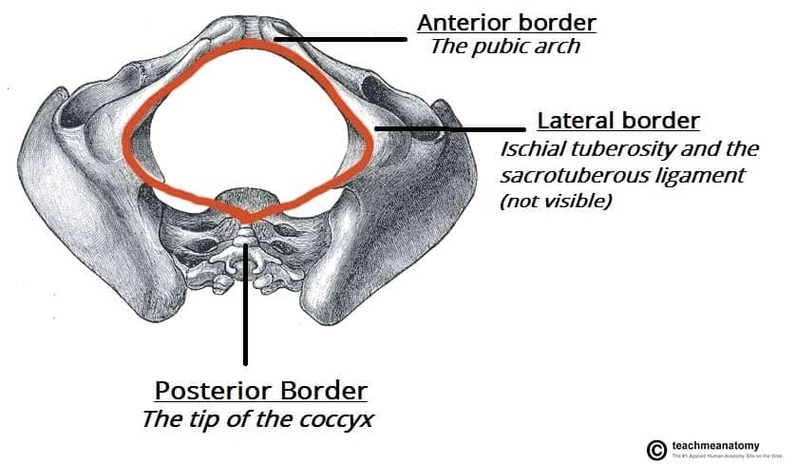
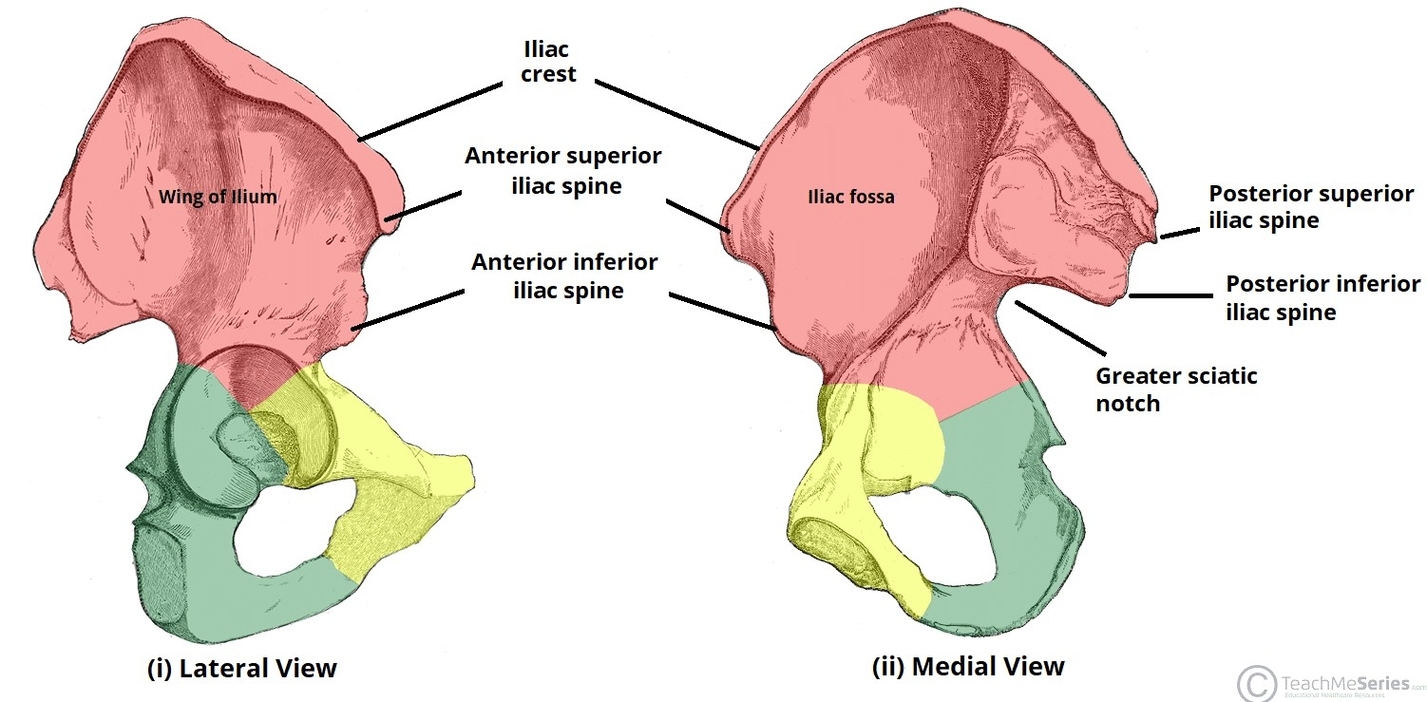
Muscles Innervated by the Accessory Nerve

Muscles innervated by the accessory nerve include the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius. The nerve provides motor control, facilitating head rotation, shoulder elevation, and posture maintenance. Knowledge of accessory nerve anatomy is essential for surgeons, neurologists, and medical students in diagnosing nerve View Diagram Muscles Innervated by the Accessory Nerve