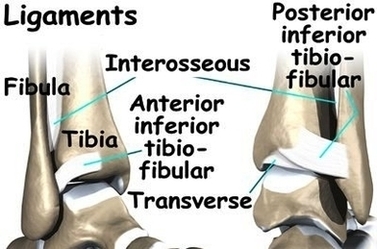
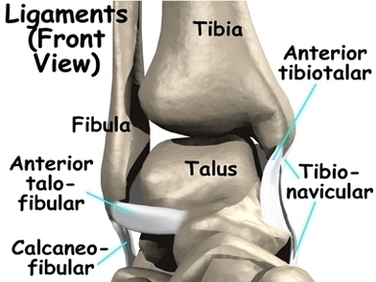
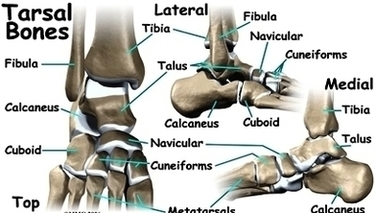
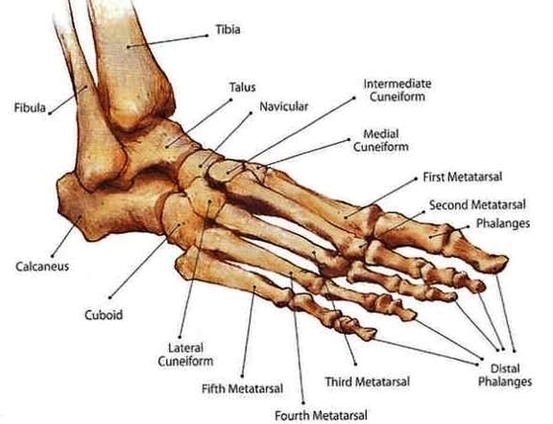
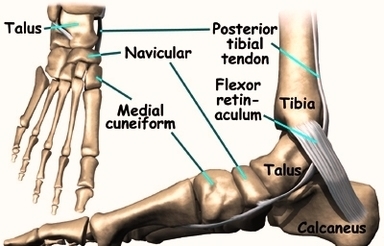
The ankle syndesmosis sits next to the ankle synovial joint, where the tibia meets the talus bone. The ankle syndesmosis is supported and held together by three main ligaments.
Injuries to the syndesmotic ligaments of the ankle or “high ankle sprains” are common in acute ankle trauma but can be difficult to diagnose both clinically and on imaging. Missed injuries to the syndesmosis can lead to chronic ankle instability, which can cause persistent pain and lead to early osteoarthritis.
Anatomy. Synovial joints are enclosed by a ligament capsule and contain a fluid, called synovium, that lubricates the joint. The ankle syndesmosis sits next to the ankle synovial joint, where the tibia meets the talus bone. The ankle syndesmosis is supported and held together by three main ligaments.
Ankle Syndesmosis Anat Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Ankle Syndesmosis Anat Image