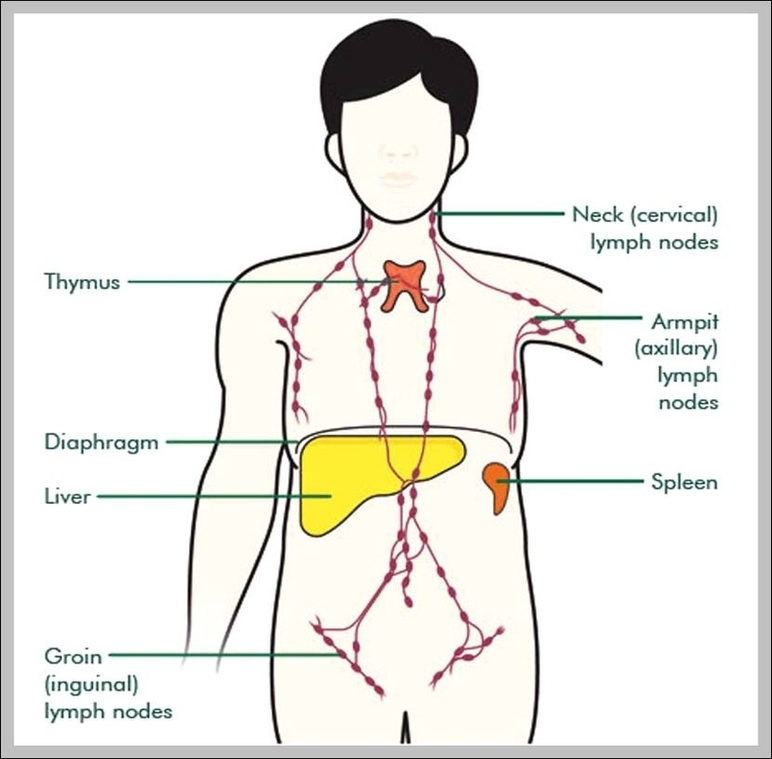
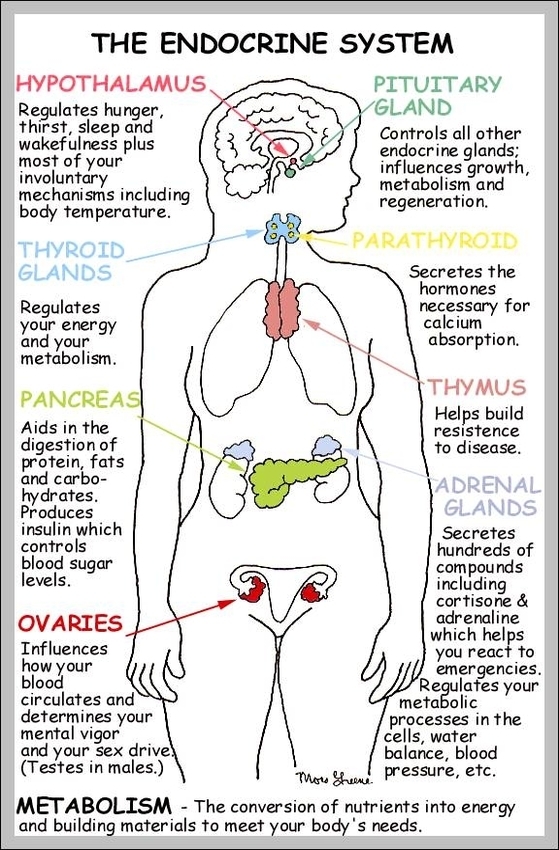
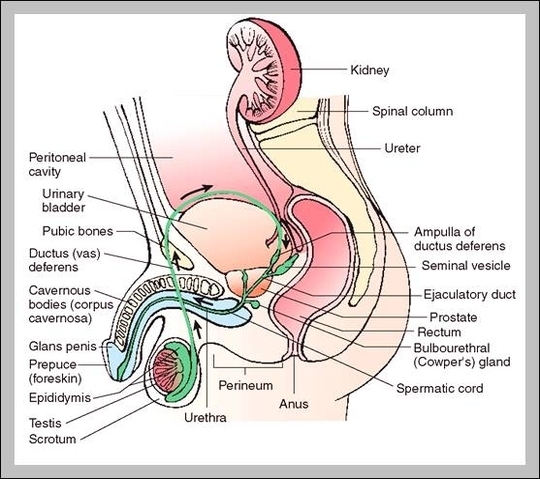
The thymus gland has an important role in immune function. One of its main secretions is the hormone thymosin. Thymosin stimulates the maturation of T cells, which are derivatives of the white blood cells that circulate our system. T cells “kill” or are cytotoxic to damaged cells.
Cells in the thymus gland (such as epithelial cells) also have receptors through which other hormones can regulate its function. The mature T cells derived have a few major roles. T cells are part of the adaptive immune system, in which each T cell has been trained to recognize a particular antigen.
The thymus gland may produce small amounts of some hormones produced in other areas of the body, such as melatonin and insulin. Cells in the thymus gland (such as epithelial cells) also have receptors through which other hormones can regulate its function. The mature T cells derived have a few major roles.
Functions Of The Thymus Gland Image Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Functions Of The Thymus Gland Image