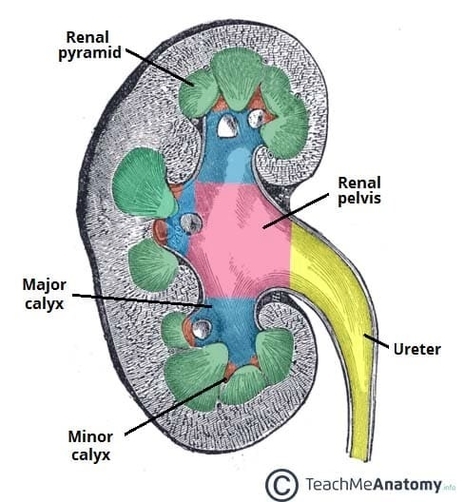
The internal structure of the kidney is organized into an outer cortex and an inner medulla, which together contain millions of nephrons that filter blood and produce urine. The cortex houses the glomeruli and convoluted tubules responsible for the initial stages of filtration and reabsorption, while the medulla contains the renal pyramids whose collecting ducts concentrate urine. These pyramids drain into the minor calyces, which merge into major calyces before emptying into the renal pelvis, the funnel-shaped region leading to the ureter. Blood flow through the kidney follows a precise pattern, with renal arteries branching into interlobar, arcuate, and interlobular vessels that supply the nephrons. This detailed internal arrangement allows the kidneys to regulate electrolytes, remove waste products, and maintain fluid balance. Internal Structure of the Kidney Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Internal Structure of the Kidney and explains the details of Internal Structure of the Kidney.
Internal Structure of the Kidney