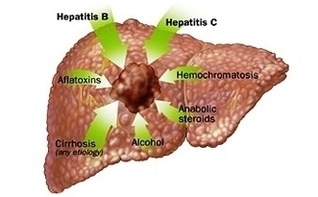
Cirrhosis of the liver is the most common cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. Increasingly, healthcare providers are seeing hepatocellular carcinoma cases in people who have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). There are other medical conditions and activities that increase your risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatocellular carcinoma occurs most often in people with chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of liver is higher in people with long-term liver diseases.
Obesity can lead to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma. The higher risk from diabetes may be due to liver damage caused by the disease.
Causes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Image