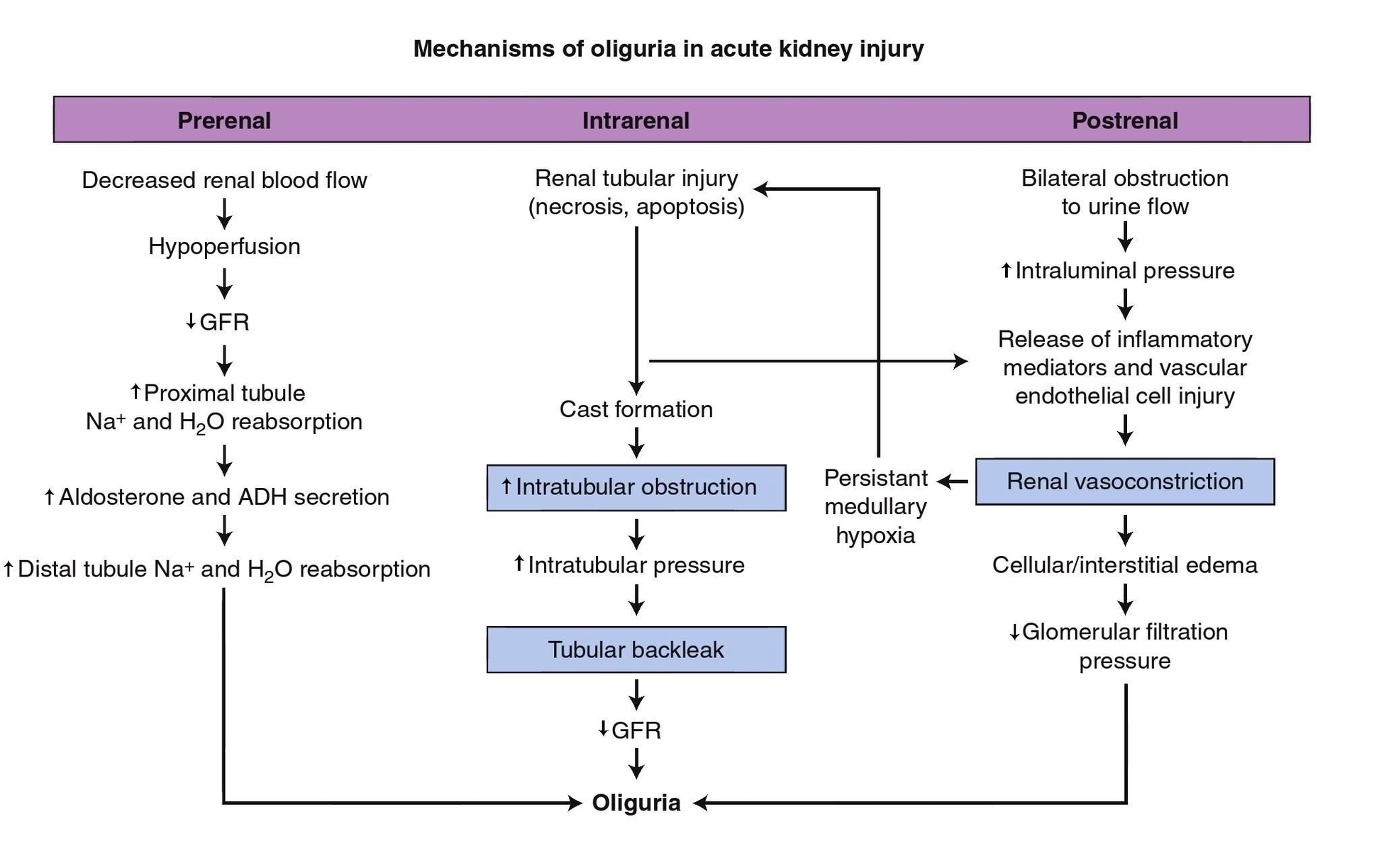
If the kidney concentration is impaired and the patient can achieve a specific gravity of only 1.010, oliguria is present at urine volumes <1000–1500 mL/day. In an attempt to standardize the diagnosis of acute renal failure, the new terminology acute kidney injury (AKI) was coined. Classifying AKI as oliguric or nonoliguric on the basis of daily urine excretion has prognostic value. Oliguria is defined as a daily urine volume of less than 400 mL and has a worse prognosis. Anuria is defined as a urine output of less than 100 mL/day and, if abrupt in onset, suggests bilateral obstruction or catastrophic injury to both kidneys. (Approximately 50-60% of all causes of AKI are nonoliguric.) This lack of a uniform clinical presentation reflects the variable nature of the injury. Classifying AKI as oliguric or nonoliguric on the basis of daily urine excretion has prognostic value. Oliguria is defined as a daily urine volume of less than 400 mL and has a worse prognosis.
Oliguria Acute Kidney Injury Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Oliguria Acute Kidney Injury