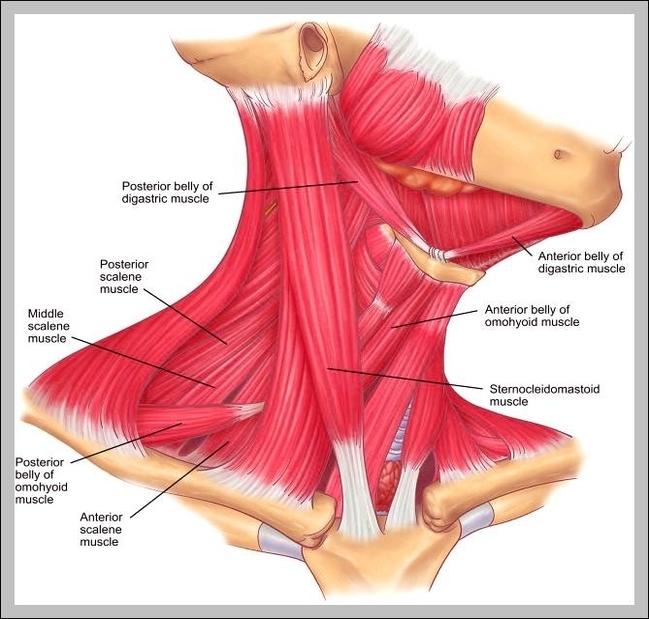
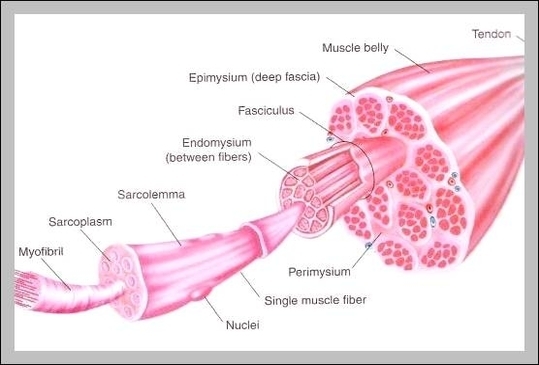
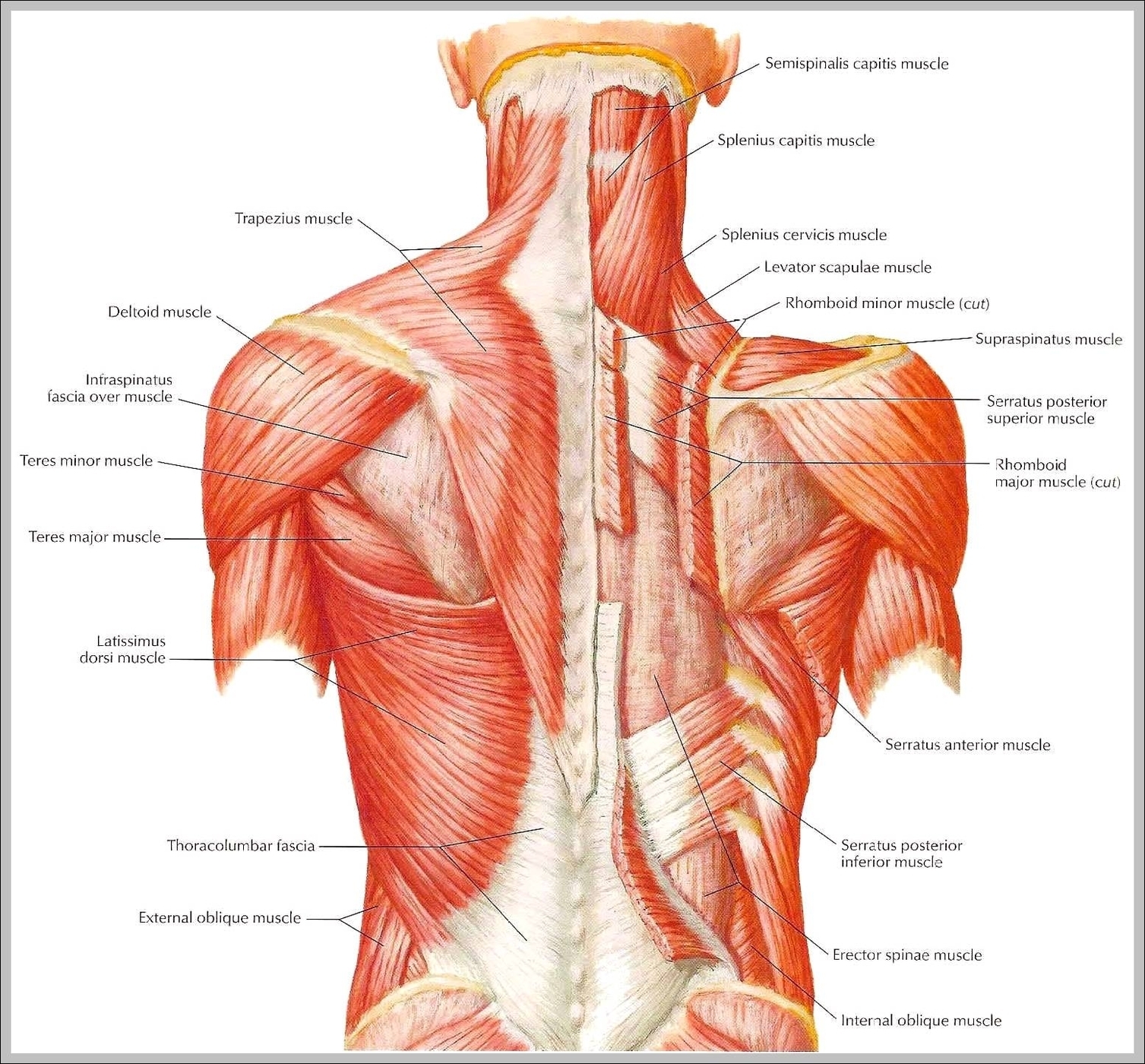
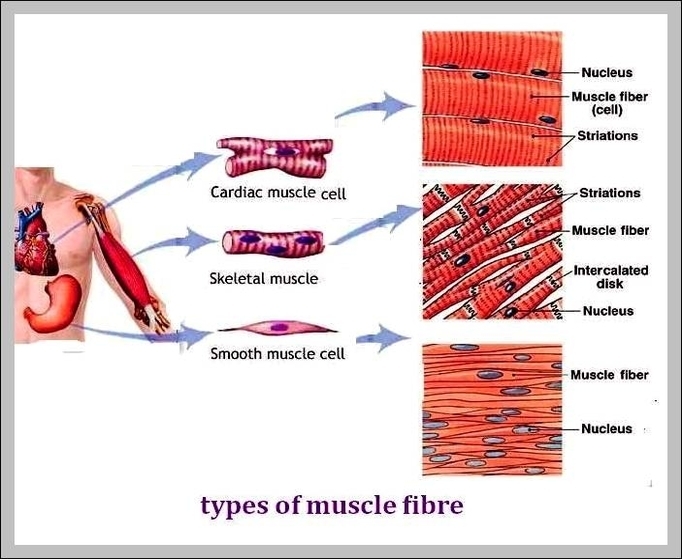
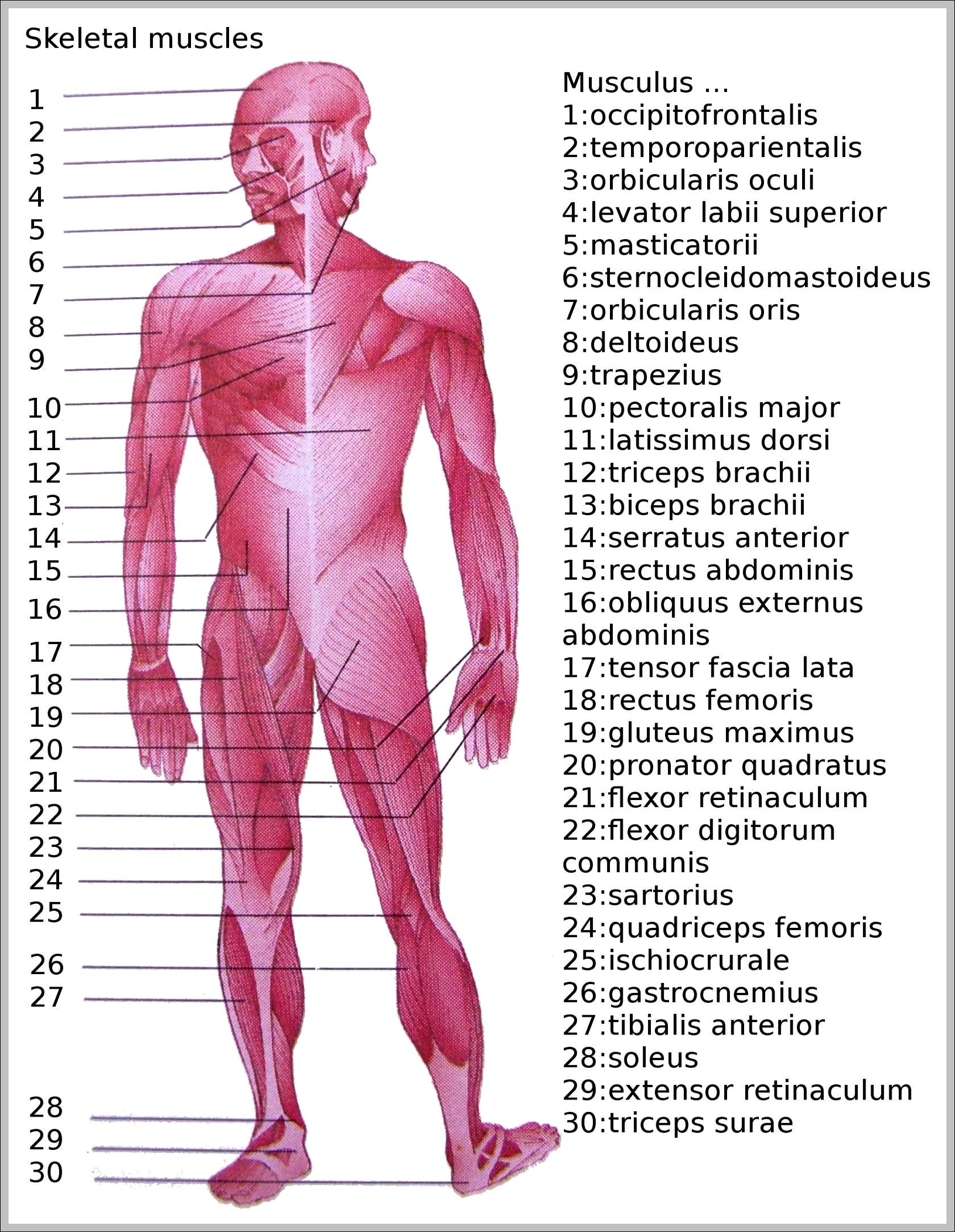
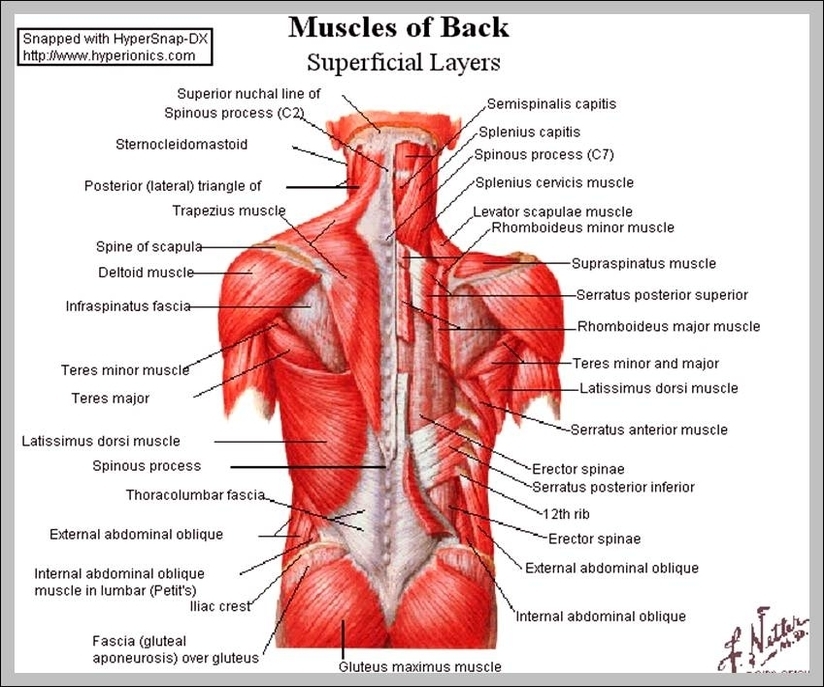
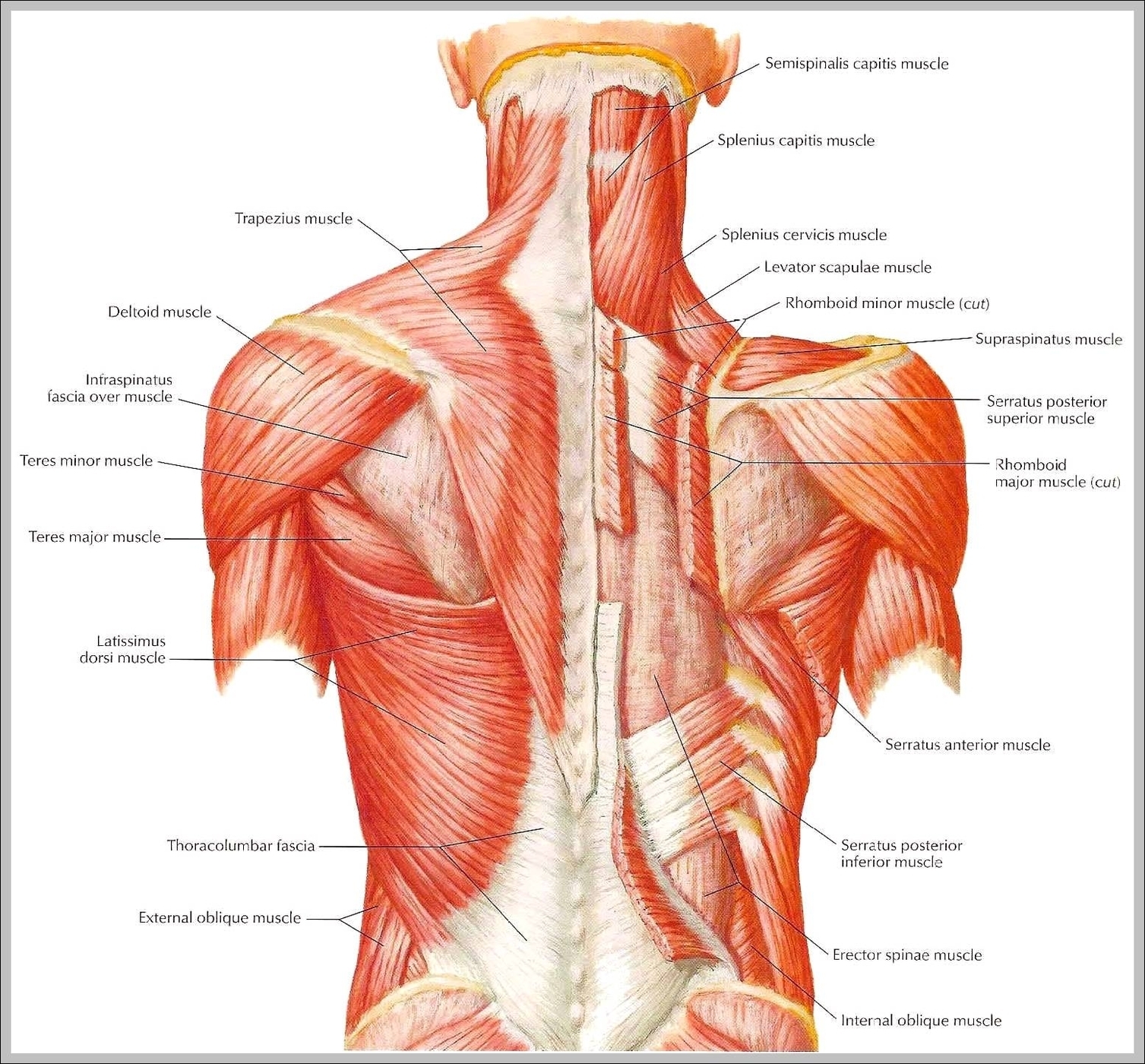
Muscles of neck. The muscles of the neck run from the base of the skull to the upper back and work together to bend the head and assist in breathing. The motion of the muscles of the neck are divided into four categories: rotation, lateral flexion, flexion, and hyperextension. Rotation describes the action of moving the head from side to side,…
These muscles and the deep muscles of the neck can be the causes of neck pain due to muscle strains, muscle tension, and other issues. A common cause of neck pain is muscle strain. This is often a result of incorrect posture.
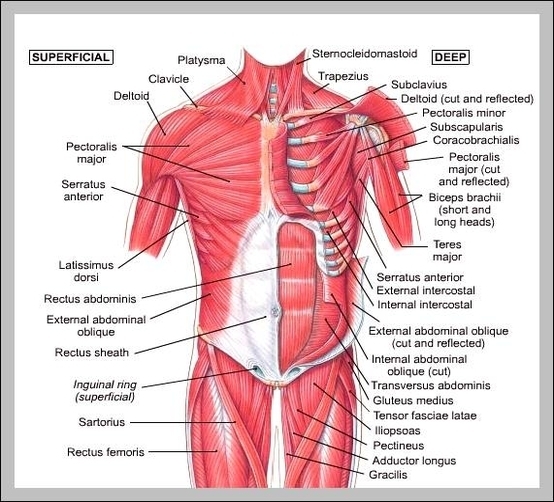
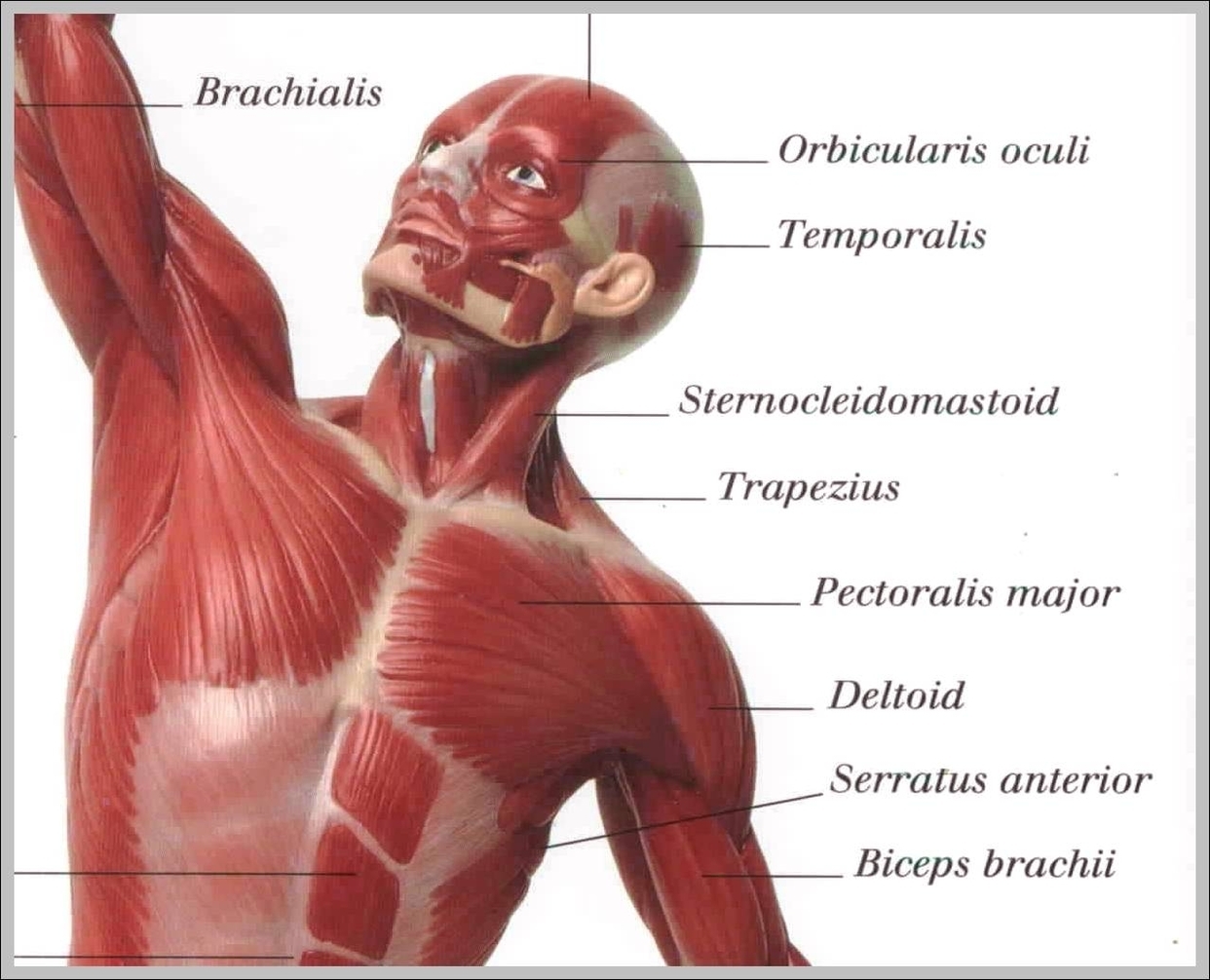
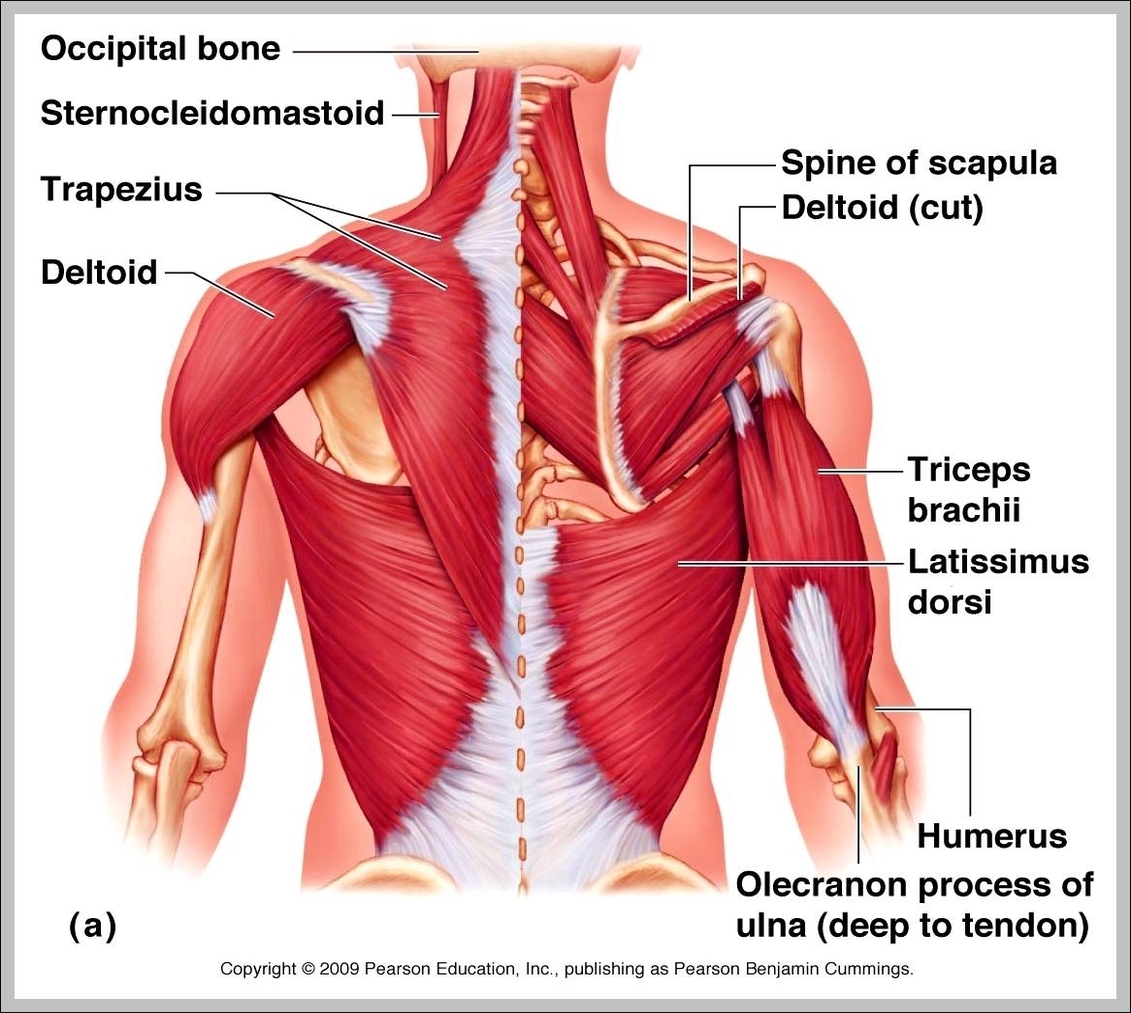
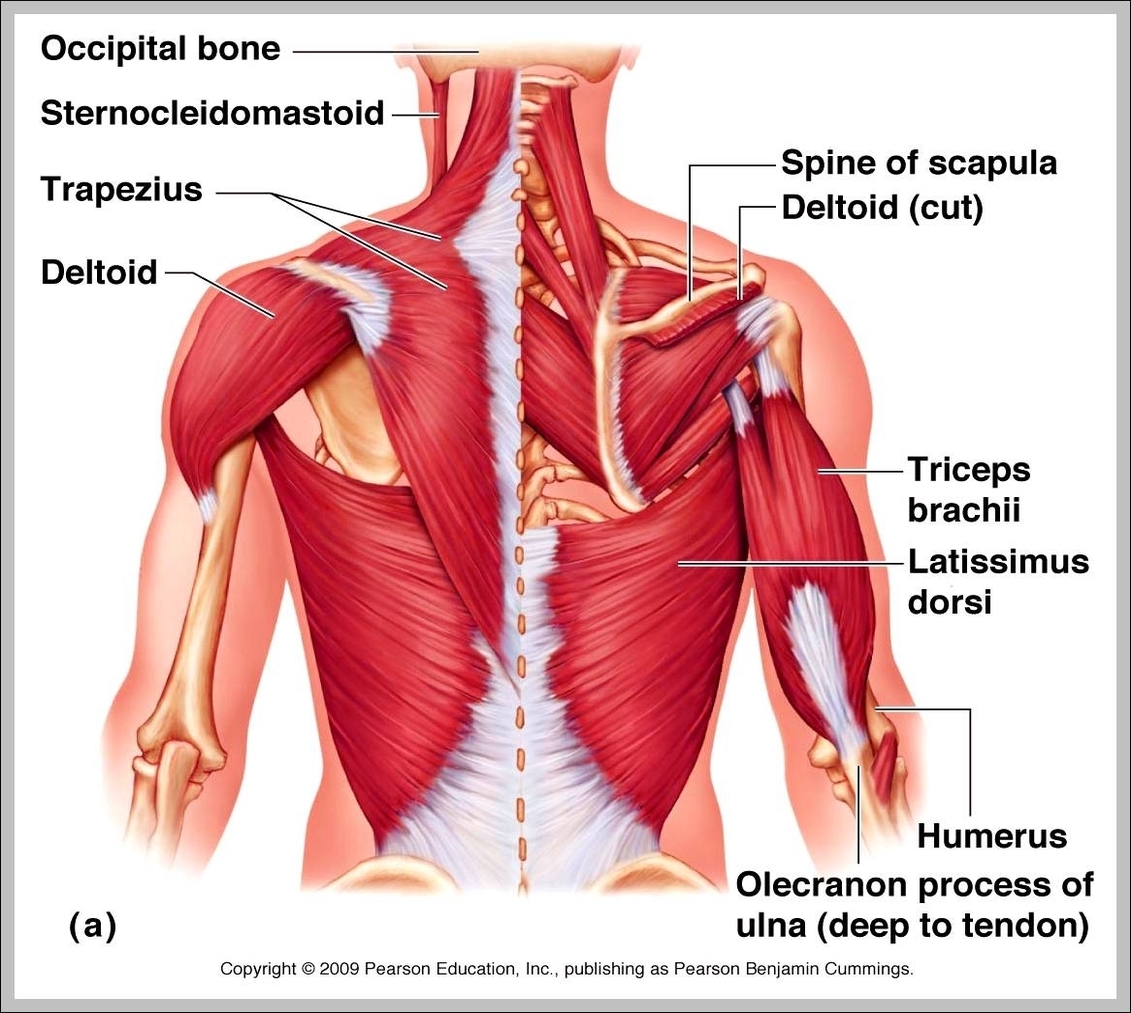
Superficial Muscles. Located underneath the platysma on the sides of the neck are the sternocleidomastoid muscles. With one on each side of the neck, these help flex the neck and rotate the head upward and side to side. They stretch from behind the ear diagonally to the center of the chest at the sternum.
Picture Of Neck Muscles Diagram - Chart - diagrams and charts with labels. This diagram depicts Picture Of Neck Muscles